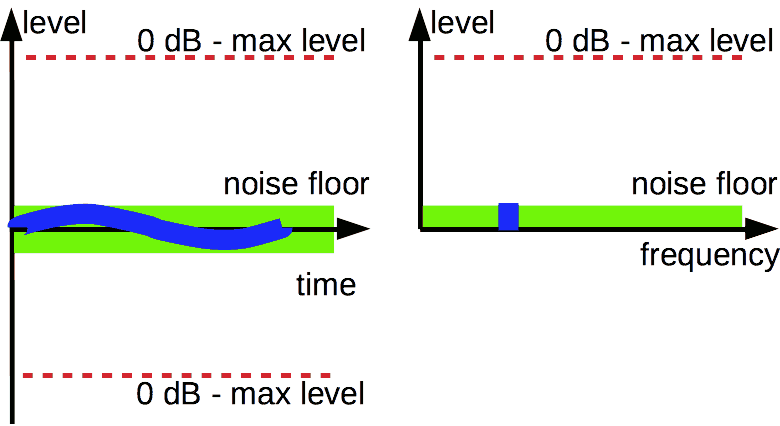
Dynamic range (DR) audio is a difference between the loudest and quietest levels of a music. It's so in the first approach. It's not that simple. Is dynamic range important? Read the explanation, measurement methods, types of the range.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.
What is dynamic range in audio?
Dynamic range (DR) in audio is measure of music expression.
This term has 2 meanings:
- Dynamic range of an audio device/software is the difference between the maximum and minimum levels of signal that provides allowable distortions.
- Dynamic range of an audio recording is the difference between the maximum and minimum loudness of a recording. It may be called a song or track's dynamic range. It is discussed in the frame of the "loudness war" (race).
The dynamic range has multiple definitions. Because minimum and maximum levels may be measured in various ways.
Read details about issues of minimum and maximum levels. The dynamic range is expressed in decibels (dB).
Back to topHow to estimate dynamic range?
When a signal passes through audio unit/software (as digital as analog) its level is limited by minimum and maximal values. Dynamic range is calculated as a difference between these levels:
DR = [Maximal Level, dB] -[Minimum Level, dB]
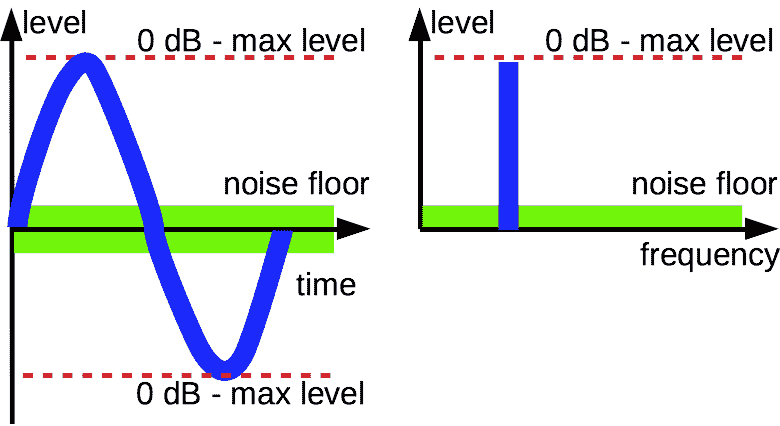
Maximum level
Maximum level of an audio signal
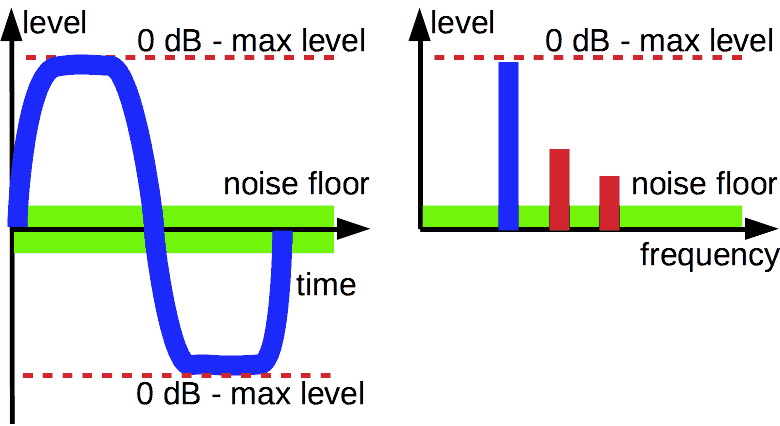
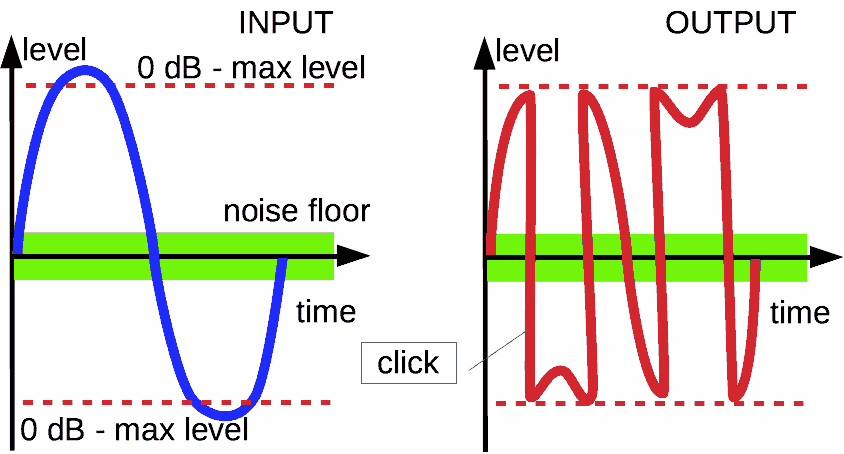
When the signal achieves an overload value, it gets non-linear distortions, that is shown in the left part of the picture as red components.
Overload audio. It is output signal for input sine
Pure digital systems (as example, software) have a sharp border between distorted and non-distorted signals.
Overload and clipping audio in simple words
Let's imagine you pour a pool. After the pool is filled, water overflows, and its level doesn't rise more.
Like it, audio signal's level at an output (water level) grows when input level is growing (water volume that enters into the pool).
The water may enter infinite time. Input audio level may grow infinitely, in theory. But, it can damage a physical device.
Output level (water level) stops growing after a device or an audio format achieved its limit (water overflow).
When the level limit is achieved, it's called clipping or overload.
Example:
16-bit signal has a maximum value: 215-1.
When signal achieves the next level (215-1), it causes overload (mathematical overflow) and 215-1 is transformed to -215 (minimum allowable value).
Digital signal overload
Such transformation can cause a loud click. To avoid the click, processing is performed in higher bit resolution. Before conversion to target (lower) bit resolution, a signal is checked to overload. If the overload is happen, the sample level is limited by maximum value. Such overload kind is the same as traditional analog one. It causes distortions without big "digital overload clicks".
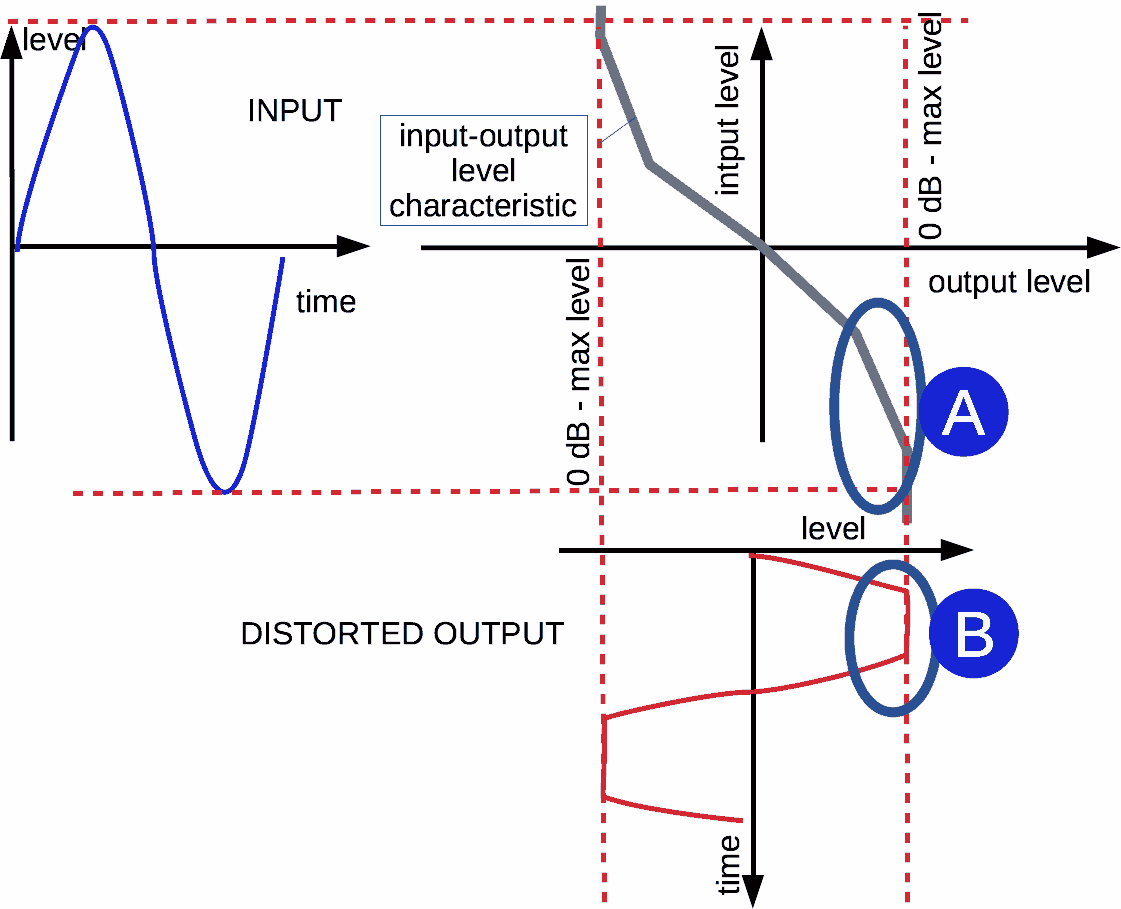
Analog overload has a smooth overload border. In the upper right part of the picture, input-output level characteristic is displayed.
Analog non-linear distortions. Input-output characteristic
When input signal level approaches to maximal limit, distortions grow too. Because the distortion intensity depends on level due to non-linearity.
Input-output level characteristics display how to output level depends on input one.
That characteristic may be linear (simple line) or non-linear, like one, displayed in the picture.
Let's look to the highest levels. A-area at the characteristic impact to waveform in area B of the output signal. So non-linearity kind in the A-area defines distortions at the output (B-area) when input signal level is about the maximal value. In other words, different levels of input signal generate various levels of distortion components at the output.
For digital signal simple binary logic ("with" or "without" distortion) may be applied.
For analog signal we can estimate various distortion levels for different input signal levels. There is a smooth overload border.
Therefore for analog signal, the maximal level may be accepted as a level that causes target distortion intensity.
Read more: Digital vs Analog audio...
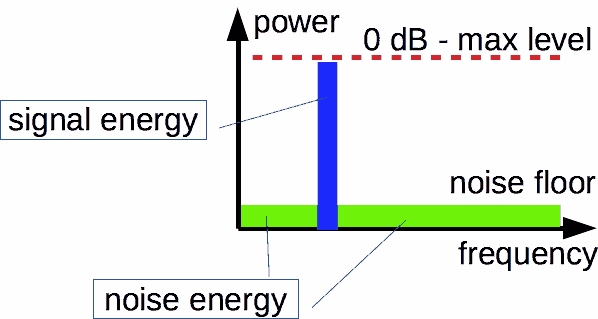
So high signal level, when distortions exceed allowable share of total spectrum energy, is accepted as maximum level.
Spectrum energy = Signal + Distortions
Minimum level
When a signal level is decreased, it achieves noise floor and hide under it. It is fairly for both digital and analog signals.
Minimum level of audio signal
There is difference in noise nature. Analog noise is a noise of electronic components. Pure digital noise is quantization noise. Captured digital signals have both kinds of noise: by electronic components and quantization. But it does not matter for minimum level estimation.
Therefore, minimum level has a different sound quality for its different values.
For pure digital units and software, quality is defined by signal/noise ratio.
For analog systems, quality is also defined by the non-linearity of the input-output characteristic of measured device.
When we consider dynamic range as the difference between a noise floor and overload level, quality estimation is lost.
When signal "drowns" in noise we can't recognize it. So such way of dynamic range estimation is too optimistic.
We want to listen minimum level in given quality. The quality is defined by signal/noise ratio.
Analog systems have different linearity for different levels. The non-linearity generates distortions: spectral products, that correlate with an original pure signal. So we must account the distortions as noise too. We can look to similar example with highest levels here.
Signal/noise ratio
Signal/noise ratio is a ratio between energies of signal and noise.
Energy may be estimated as a square of a power spectrum.
Power is level2.
Signal/noise ratio at the power spectrum
If we can localize signal spectrum, rest spectrum we can accept as noise and distortions.
It is a reason why we can't use music as a test signal. Music have dense spectrum and it is almost impossible to separate noise, distortions and an original signal.
Also, using complex signals (multi-tones, as example) can cause issues of signal and noise separation.
We can step-by-step reduce the noise level to achieve given signal/[noise and distortions] ratio. This level is accepted as minimum.
Signal energy (square) calculation does not matter. But band of the signal may be accepted differently for different methods.
Also, noise and signal energies may be calculated accounting psychoacoustics: equal-loudness contour.
Back to topDynamic range for a recording (song, track). Loudness range
Dynamic range (loudness range) for song is based on statistical distribution of loudness measurements.
Its calculation method try avoid of impact of too low-level fragments (background noise) or short high-loudness events.
Back to top
Frequently asked questions
What is dynamic range in audio? What is audio dynamic range?
Dynamic range is a property of an audio device or audio processing. Also, a music-recording-level range is considered as dynamic range.
Read more...
What is dynamic range sound?
In the first approach, dynamic range of sound is difference between quietest and highest places in a recording.
Read details...
What is dynamic range in simple terms?
Dynamic range is a difference between minimum and maximum allowable values in some domain: audio, video, photo, etc.
What is dynamic range in dB?
Dynamic range is a difference between values. Difference may be measured in dB to better mind perception.
Is dynamic range important audio?
Does audio dynamic range matter?
Why is dynamic range important?
Dynamic range is very important for musical devices. It refer to sound quality directly (noise floor, intermodulations, non-linear distortions).
Dynamic range and average level of an audio file, is important in sequential file playback. It impacts to loudness integrity of such audio stream in TV, broadcasting, home listening.
Dynamic range of a music file impacts to the piece emotional expression. In cinemas soundtracks, it may impact to listening comfort due to difference between dialogue and sound effects.
Read about audio file's loudness normalizing...
What is dynamic range and why is it important?
Dynamic range is loudness range of music recording's fragments. If the difference is small the music or movie soundtrack is not expressive.
Dynamic range of a device is important too.
Read more...
How do you describe the dynamic range of a song?
Dynamic range of song describe one of kind of music expression. The kind is achieved via loudness difference between different timeline places of the track.
Read more...
Is higher dynamic range better audio?
Higher dynamic range of audio device provides better sound quality.
Dynamic range of an audio file describe expression level of a musical piece. However, it does not refer directly distortions and sound quality.
What is a good dynamic range?
As measurement kind, the dynamic range may have different interpretations, that is bound with psychoacoustics.
Also, dynamic range depends on music genre.
Approximately, we can consider the minimum allowable signal/noise ratio of lowest signal like to analog devices - about 40...60 dB. It is the quietest place of a musical piece.
So, to found the difference between maximal loudness and noise floor, we should add to the difference between the quietest place and maximal loudness of the piece to the SNR.
Examples:
- When the difference between fortissimo and pianissimo (maximum and minimum loudness) is 60 dB: dynamic range is 60 dB and difference between maximum loudness and noise floor is 60 dB + [40...60] dB = 100 ... 120 dB.
- When the difference between fortissimo and pianissimo (maximum and minimum loudness) is 80 dB: the dynamic range is 80 dB and the difference between maximum loudness and the noise floor is 80 dB + [40...60] dB = 120 ... 140 dB.
What is a good dynamic range for audio interface?
As rule, in a specification of audio interface we can see noise floor. -115 dB and more is a good level.
What does dynamic sound mean?
It is sound with loud (or too loud) and quiet (to quiet) places.
How do you find the dynamic range?
Dynamic range may be measured via special hardware and software tools.
What should my dynamic range be? Whats a good loudness range?
Dynamic range (loudness range) should provide comfortable listening and allow bring musical piece details.
Thus, recording dynamic range depends on music genre. In instance, it's measured average 4.0 LU for Hip Hop, 6.4 LU for Pop, 9.9 LU for ballad, etc. Classical music and jazz requires maximum range.
If you produce music, you should refer to your ears in target loudness range: quiet places should be listenable, loudest one should not cause distortions. Reducing the range should not cause character losses of a music.
Is dynamic range compression good?
Dynamic range compression is used to manipulate music expression. It's applied as to separate instruments as to full mix.
In home theater applications, dynamic range may be compressed to avoid too load and too quiet places in an audio stream.
Of course, the compression should be applied properly to avoid unpleasant-listening effects.
How can I increase my dynamic range of music?
Dynamic range may be increased via an expander (audio processor type). It may be done as hardware as software.
Better way, it dynamic range increasing during mixing and postproduction of music.
Should DRC be on or off?
Dynamic Range Control (DRC) is option of home theater / AV-receiver. If you desire listen movie's soundtrack as is, turn it off.
If you don't like quet dialogs and too loud music and sound effects, turn DRC on.
What dB level should I mix at?
It is recommended to do audio track mixing at 85...90 dB SPL of monitor loudspeakers. It's explained better ear frequency response according to Fletcher Munson Curve [*].

Back to top
Conclusions
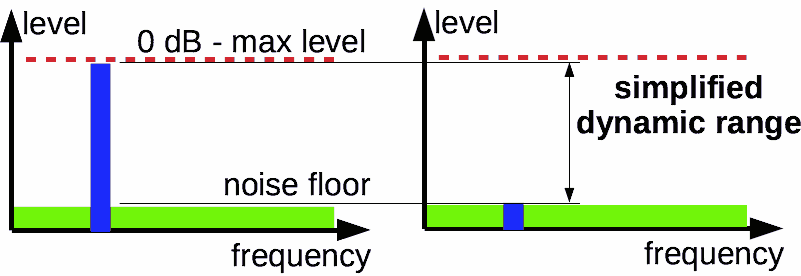
- Simplified dynamic range is a difference between signal that causes overload and noise floor.
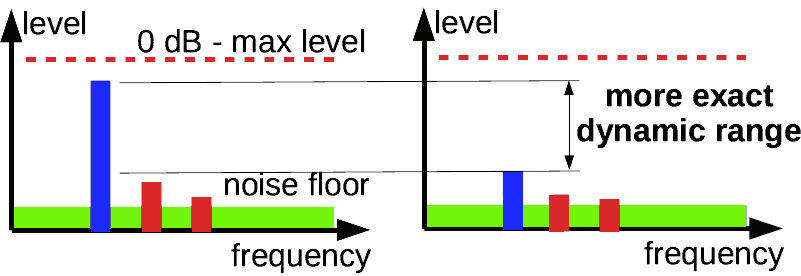
- Estimation of audio dynamic range should take into account sound quality.
- Dynamic range by goal #2 has lesser value than simplified definition by goal #1.
Simplified dynamic range estimation
Dynamic range estimation, taking into account sound quality
Back to top
References
Audio Basis - articles about audio
Back to top