Read about issues of digital-to-analog conversion audio and ways for improving the quality of conversion.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.

Bases of analog signal restoring from digital form
Simplest PCM digital-to-analog converter (DAC) contains:
1. Circuit conversion of a digital sample (number, value of electrical voltage) to electrical voltage.
2. Analog low-frequency filter.
Still no robust proof that we hear ultrasound. According to the Nyquist theorem, 40 kHz sample rate + band reserve is enough for transient band of the low-frequency filter.
So, we have 44.1 kHz sample rate standard. However, real implementation of restoring audio stuff (especially, low-resolution) raises some issues of quality.
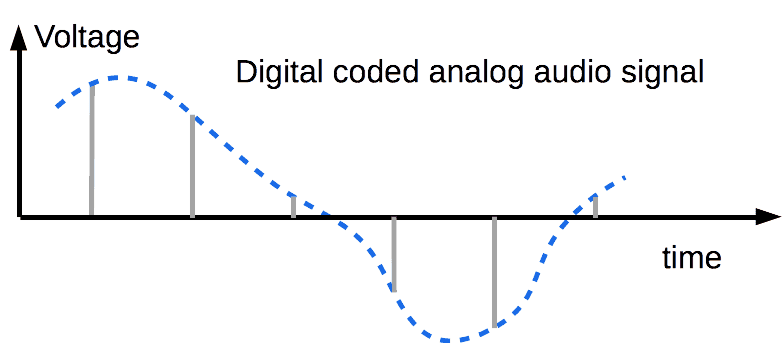
A spectrum of audio-sample sequence that is converted to voltage (stairs) consists of several parts:
1. useful spectrum in the low half of the spectrum.
2. mirrored and flipped useful spectrum at the high half of the total spectrum.
In this article, graphs have no real scales. The scales are intended for clearer explanation.

An ideal analog filter should:
1. fully pass by useful spectrum {0 … 20 kHz}
2. fully eliminate mirrored spectrum {20 kHz…[sample rate]}.
Analog filter provides a transient band.It's area between pass and stop frequency bands.

Analog filter’s frequency response is showed as the grey line.
Back to top
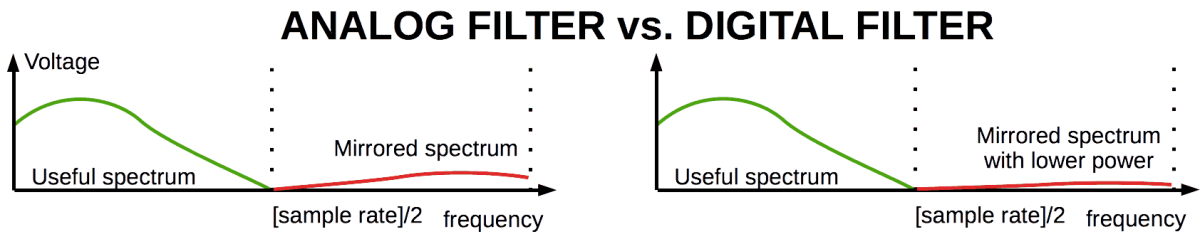
Digital filter vs analog filter
In a DAC and ADC, digital and analog filters are embedded.
Any filter types cause oscillations at output on input signal change. These oscillations has some duration before disappearance.
Filter with finite impulse response (FIR filter) has output oscillations before input signal occurs. It's called "pre-ringing". The strange phenomenon happens due to delay between input and output. Such filter has linear phase response. I.e. it doesn't change signal in the time domain.
FIR filter may be implemented without pre-ringing. But, phase response is not linear, that causes time domain-distortions. It means, different frequencies have various time delays when pass through the filter. Such filters are called "minimum-phase filters".
In comparion with analog filters, digital filter may have almost ideal and more manageable features. Digital filters don't require tuning when they copied at a factory for device serie.
Analog and digital filters has some difference in the sound. Digital filters can cause lesser distortions and more qualitative cutting excessive frequencies. Analog filters may be preferable by personal taste.
Back to top
Issue of restoring to analog signal is real life
The DAC’s analog filter has enough sloping transient between the pass and stop bands.
And it can’t suppress mirrored spectrum deeply.
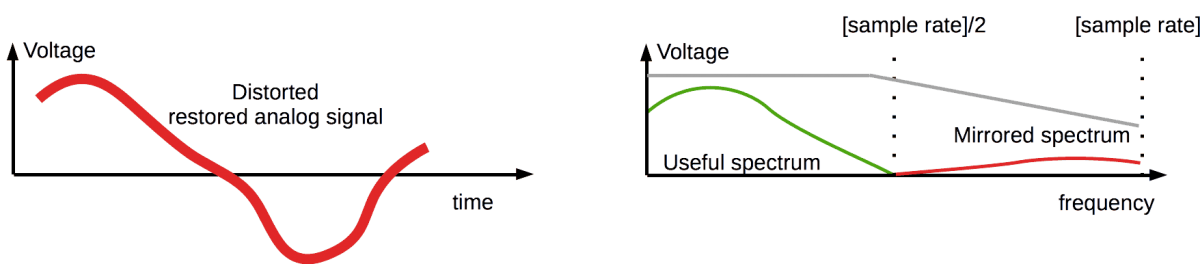
For the ideal analog part of playback apparatus, mirrored spectrum is harmless.
But real apparatus have non-linear distortions in analog parts of DAC, amplifiers, speakers, etc.
It leads to the generated audible products like mirrored and distorted spectrum. The phenomenon is called "intemodulation".
Due to non-linear distortions, the mirrored spectrum in the ultrasound range is reflected at low frequencies.
The kind of reflection depends on the non-linearity type. Here you can see the example of a special case...

How to decrease the distortions in audible range?
Level of the mirrored distortions in the audible range depends on amplitude/power of mirrored spectrum. All that is placed at the upper half of the spectrum of analog signal that is restored from the digital one.
Therefore we should decrease the power of mirrored spectrum.
We can’t significantly improve the real analog low-frequency filter of DAC. It will slope for modern hi-fi demands.
However, we can apply oversampling
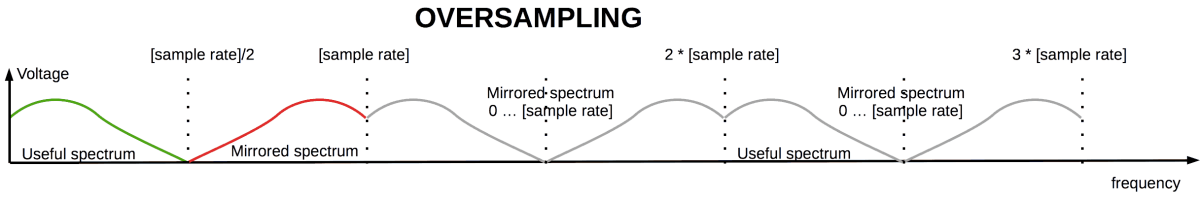
and steep digital filter before analog.
Oversampling create additional periodical mirroring of {0…[sample rate]} area at frequencies above original sample rate.
Digital filter, if it's better than analog one, can suppress artifacts about higher limit of audible range.

Now analog filter should suppress highest frequencies in the oversampled spectrum.
Highest frequencies are more suppressed by analog filter. And the analog filter works the best way for this case.

Hardware vs. software oversampling-filtration
Realtime-hardware-digital-oversampling filter can have computing limitation due restricted resources on chip.
So there may be slope transient band issues too.
As alternative can be used additional offline or inline oversampling filter released in personal computer software.
Computer have big calculation power, including floating point precision.
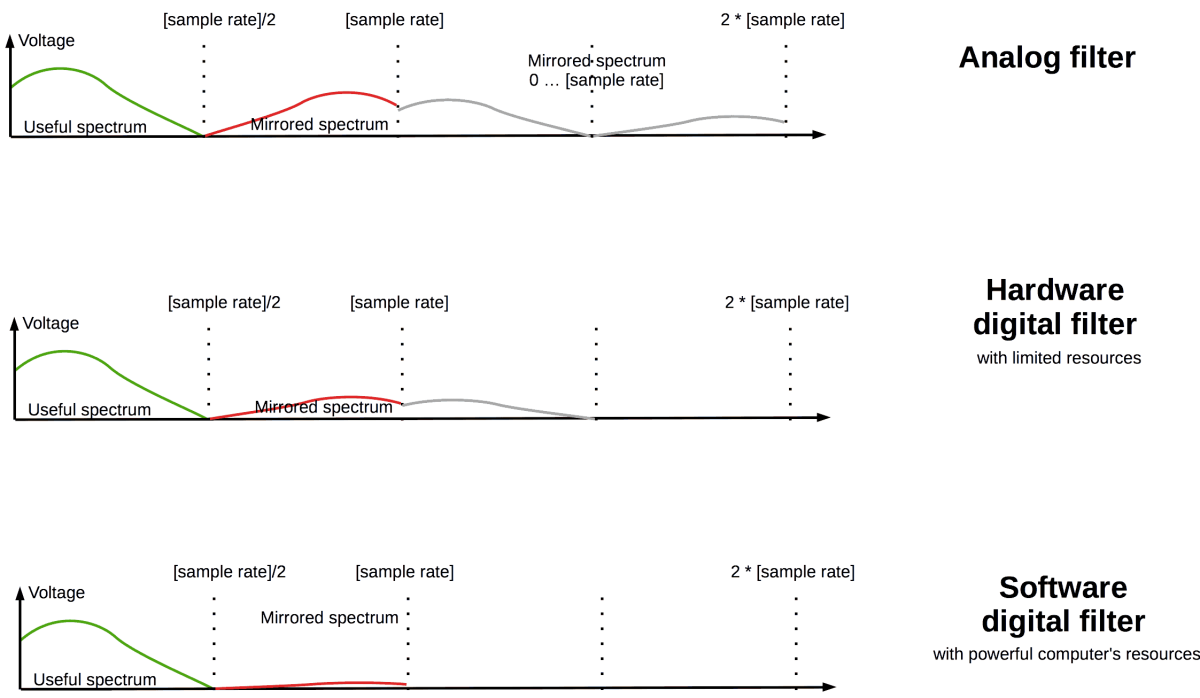
There DAC’s digital-oversampling and analog filters applied to preliminarily filtered spectrum.
Pre-filtration oversampled audio stuff allow to decrease the mirrored spectrum level even more.
AuI ConverteR have resampling filter modes:
1. "Optimized" (cutting all above 20 kHz) or "Optimized G5" with improved filtering;
2. "Non-optimized" (traditional resampling mode);
3. "Non-optimized wide" (band up to 100 kHz for ISO, DSF, DFF conversion).
Click Settings button in AuI ConverteR's main window. Appear Settings window.
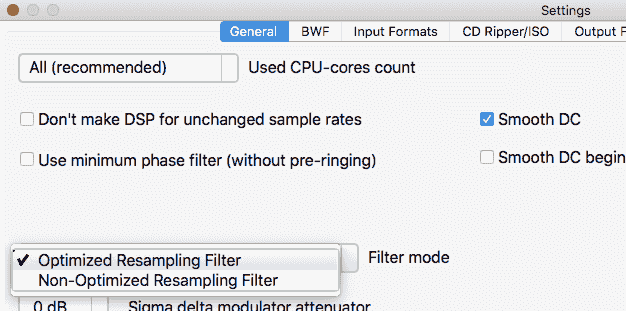
There need select mode via Filter mode list.
Read more...
Back to topInline vs. offline software oversampling-filtration
Inline filter can be released in audio player software. Audio file played without any pre-processing.
Inline conversion has next issues:
1. possible lack of computer’s performance for realtime processing.
2. consuming of significant part of total performance.
3. consuming additional electric energy for hard work. There rise additional heating (and sometimes cooling fan noise) matter each time of playback.
Offline filter solve the issues:
1. For old computers playback of pre-oversampled-filtered files is easier.
2. Released computing resources for other tasks (graphics, music database, network, etc.).
3. Economy of electrical energy during playback with lower noise of cooling fans of the audio computer.
Offline filter can be applied in audio converter / resampler. Pre-oversampled-filtered files used for playback in bit-perfect mode (unmodified binary content sent to DAC).
Conclusions
1. Quality of restoring analog signal from digital depend of sharpness of DAC’s analog filter.
2. Sharpness of analog filter technically restricted.
3. It solved via digital pre-oversampling-and-filtration builtin DAC.
4. In some cases, for better result may be used additional software pre-oversampling-and-filtration.
5. Inline realtime oversampling-filtration don’t demand pre-converting audio files.
6. Offline conversion allow apply heaviest oversampling-filtration on old computers and save electrical energy during playback.
- What is Jitter in Audio. Sound Quality Issues >
- 64-bit audio processing. Necessity or redundancy >
- What is Audio Converter >
- How to Choose the Best Audio Converter Software >
- What Is Ringing Audio >
- What is dithering audio? >
- Bit-Depth Audio and Harmonic Distortions >
- Audio as Optics >
- Where is the Limit of Audio Quality? >
- All what you need to know about loudspeakers >
- Power Conditioner for Audio. It's real advantage? >
- True Gapless Conversion (seamless album conversion for operas, live concerts, etc.) >
Audio Basis - articles about audio
Back to top