At last I decide to make lite research how PCM to DSF conversion impact to audio quality.
For checking I used well known third party analyzing software Rightmark Audio Analyzer (RMAA). My version of the software doesn't supporting DSF format, so I was forced to make more "hard" experiment.
About these tests
These tests don't cover whole audio comparison of DFS and PCM file formats.
Results can depend on used measurement and conversion software, playback hardware and software, other factors.
Here we can consider audio characteristics only measured and as measured by RMAA. Author haven't information about metrology certification of RMAA.
Everybody can repeat it at home with free software available for download.
Author don't claim final true. For figure more full and correct need make more researches.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.
About analyzing software
RMAA allowed automatically measure such characteristics of apparatus and software as frequency response, noise level, total harmonic distortions and etc.
The software create test and calibration WAV-files. Test file used for pass through checked software. In output the software created output file. The output file load to RMAA for analyzing.
Output file must have sample rate same to the test (input) file.
How are DSF and PCM compared
Thus for testing I use:
1. WAV (PCM 44 kHz/32-bit float) to DSF (1-bit/D64/D128) to WAV (PCM 44 kHz/32-bit float) conversion.
2. WAV (PCM 44 kHz/32-bit float) to PCM (352 kHz/32-bit float) to WAV (PCM 44 kHz/32-bit float) conversion.
So we can check not only PCM to DSF conversion. But total impact to sound quality of full cycle PCM-DSF-PCM. It's two times more "hard" experiment! :)
For more wide comparison DSF vs. PCM I also check responses for zero digital processing. I loaded to RMAA for analyzing source test 32-bit float file (without any processing). Also I created and loaded 16- and 24-bit test files to RMMA for comparing with PCM-DSF-PCM conversion.
About DSF conversion software
I did conversion PCM to DSF to PCM with maximal AuI ConverteR 48x44 PROduce-RD under MacOS. Of course conversion with AuI under Windows or other Mac operation systems don't impact to conversion quality. The converter do all the processing inside. System audio resources don't touched. Also possible use AuI's FREE edition for such converting.
Experiment results
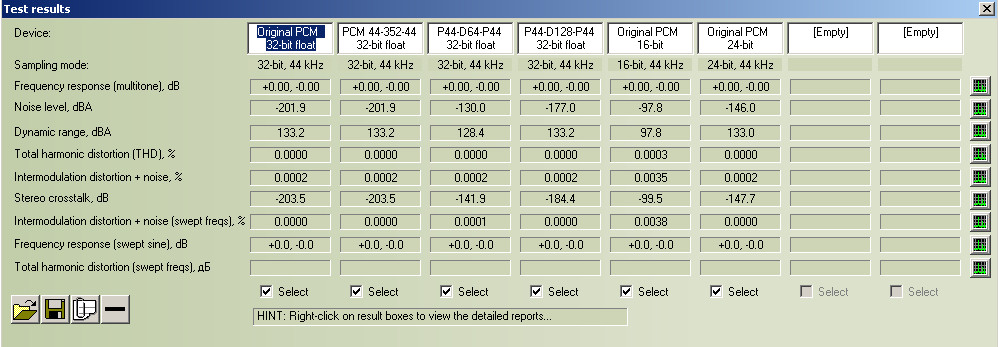
Here we can see results of comparison in RMAA's analyzing window
Comparison DSF vs. PCM (click for enlarge)
Responses without processing (ideal responses)
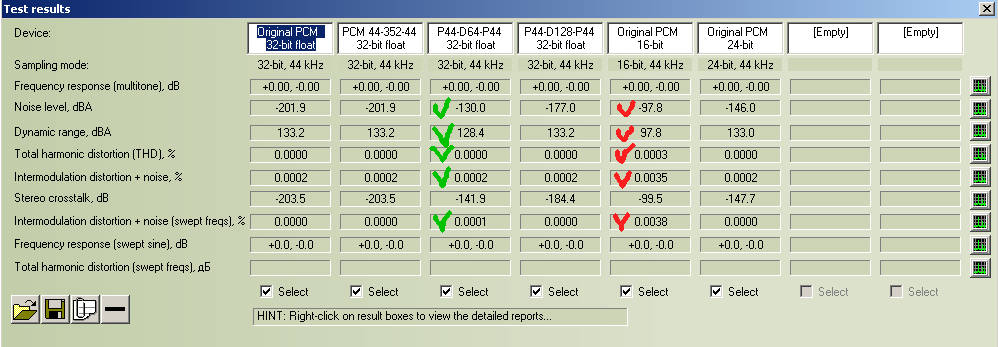
First column "Original PCM 32-bit float" showed characteristics of test file (44 kHz/32-bit float) without any processing.
We can note:
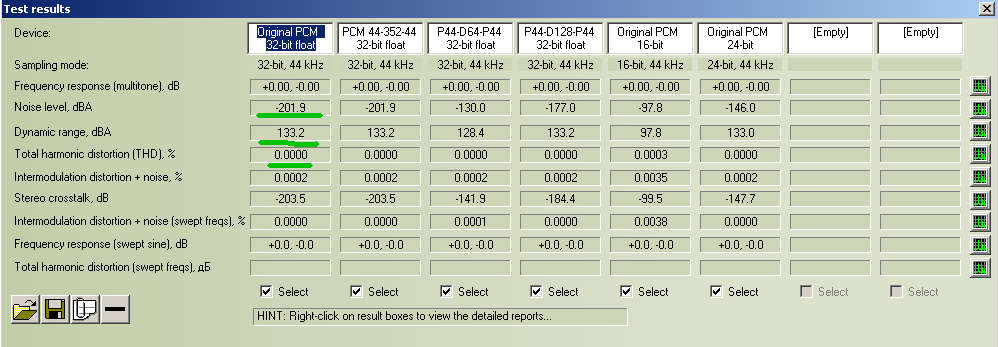
1. low level of noise (-201.9 dBA),
2. low level of Total Harmonic Distortions (THD) - better 10-4%.
3. Wide dynamic range 133.2 dBA.
How PCM oversampling/downsampling audio impacts
Second column "PCM 44/352/44 32-bit float" showed characteristics of result file (44 kHz/32-bit float) after processing WAV (PCM 44 kHz/32-bit float) to PCM (352 kHz/32-bit float) to WAV (PCM 44 kHz/32-bit float).
We can't see any impact to source test file during such processing. Thus if the impact is exists, it out of measurement range of RMAA.
What PCM to DSF (DSD64) conversion impacts
Next column "P44-D64-P44 32-bit float" showed characteristics of result file (44 kHz/32-bit float) after processing WAV (PCM 44 kHz/32-bit float) to DSF (2.8 kHz D64/1-bit) to WAV (PCM 44 kHz/32-bit float).
1. Noise level increased from -201.9 to -130.0 dBA (worse 71.9 dBA).
2. Dynamic range decreased from 133.2 to 128.4 dBA (worse 4.8 dBA).
3. Intermodulation distortions + noise increased from 0.0000 to 0.0001 % (worse 0.0001 %, that possible placed within the measurement error).
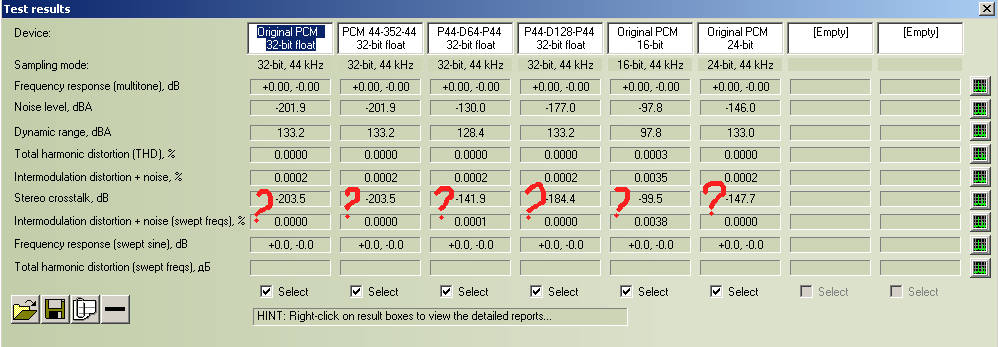
4. Stereo crosstalk increased from -203.5 to 141.9 dBA (worse 61,6 dBA, read below about stereo crosstalk measurement particularity).
About Stereo Crosstalk feature
Stereo crosstalk is independence of stereo channels from one another.
I'm using RMAA as "black box". I don't (while) learn it's methods of measurement.
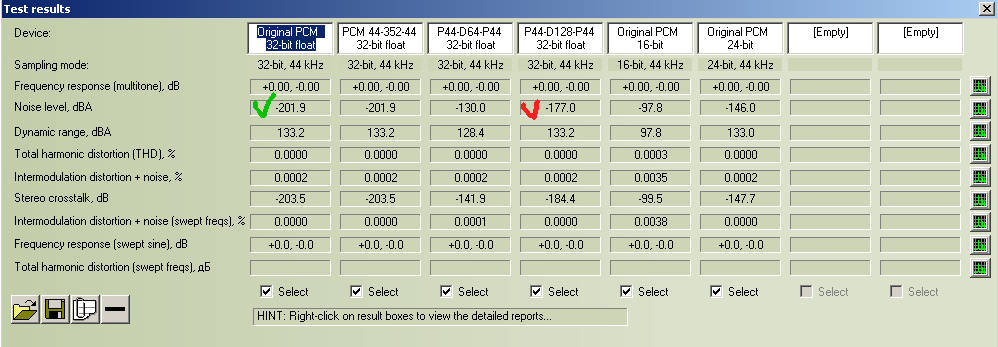
I know what stereo crosstalk for software (and for original non-processed files) must be infinite.
But into RMAA for original (non-processed WAV) I see -203.5 dB. Why? Both channels of source file must be generated independently.
If we will generate one channel sine and other channel absolute silence in software, audio data of "sine" channel don't come to "silence" channel anyway.
Also I know what AuI ConverteR process all channels of files absolutely separately.
So why RMAA don't show infinite stereo crosstalk for original files and AuI ConverteR?
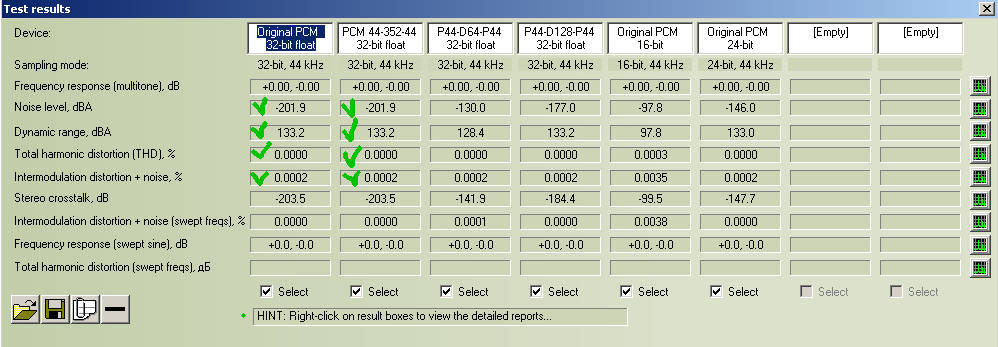
See to original 32-bit float WAV level of noise -201.9 and crosstalk -203.5 dB.
See (column "Original PCM 16-bit") to original 16-bit float WAV level of noise -97.8 and crosstalk -99.5 dB
See (column "Original PCM 24-bit") to original 24-bit float WAV level of noise -146.0 and crosstalk -147.7 dB
Difference between noise and crosstalk is -1,6 ... -1,7 dB for all 3 cases.
So I suppose what RMMA's method of stereo crosstalk measurement bound to noise level (theoretically it must be so too).
Thus we can't consider stereo crosstalk characteristic for software processing channels absolute separately (like AuI ConverteR).
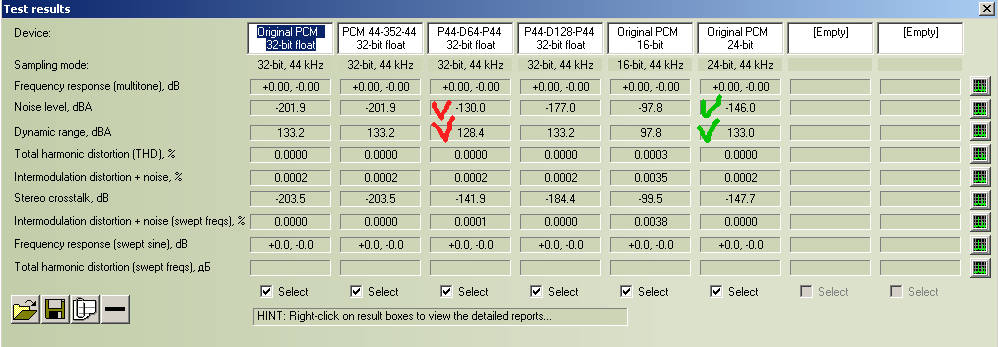
DSF (D64) with PCM 16-bit comparison
For comparison we can see to non-processed 16-bit PCMs (columns "Original PCM 16-bit").
1. Noise level D64 (-130 dBA) better non-processed 16-bit PCM (-97.8 dBA).
2. Dynamic range D64 (-128.4 dBA) better non-processed 16-bit PCM (97.8 dBA).
3. Total harmonic distortions D64 (0.0000%) better PCM 16-bit (0.0003 %).
4. Intermodulation distortion and noise D64 (0.0002%) better PCM 16-bit (0.0035 %).
DSF (DSD64) with PCM 24-bit comparison
For comparison we can see to non-processed 24-bit PCMs (column"Original PCM 24-bit").
1. Noise level D64 (-130 dBA) worse non-processed 24-bit PCM (-146.0 dBA).
2. Dynamic range D64 (-128.4 dBA) worse non-processed 24-bit PCM (133.0 dBA).
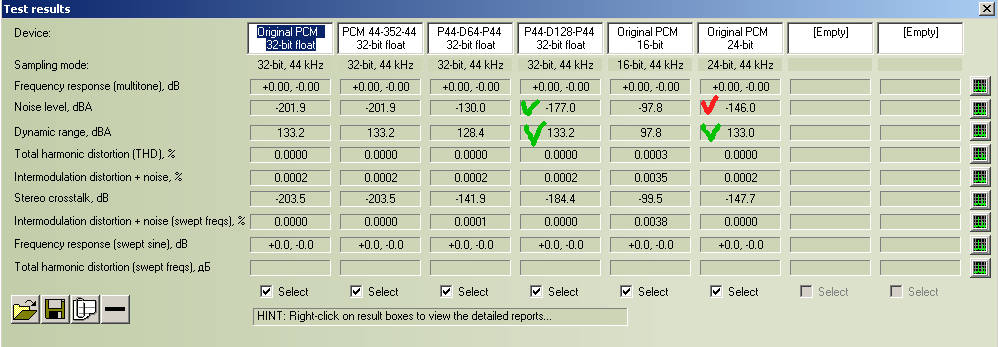
DSF (DSD128) with PCM 24-bit comparison
For comparison we can see to non-processed 24-bit PCMs (column"Original PCM 24-bit") and PCM-D128-PCM column "P44-D128-P44 32-bit float".
1. Noise level D128 (-177 dBA) better non-processed 24-bit PCM (-146.0 dBA).
2. Dynamic range D128 (-133.2 dBA) close non-processed 24-bit PCM (133.0 dBA).
DSF (DSD128) with PCM 32-bit float comparison
For comparison we can see to non-processed 32-bit float PCMs (column"Original PCM 32-bit float") and PCM-D128-PCM column "P44-D128-P44 32-bit float".
1. Noise level D128 (-177 dBA) worse non-processed 32-bit float PCM (-201.9 dBA).
Conclusions
Before reading the Resume I recommend re-read About these tests :)
Results can depend on used measurement and conversion software, playback hardware and software, other factors.
Here we measure characteristics by RMAA and compare it. But we must make audio tests and instrumental tests via certified software.
If we can consider CD as enough qualitative lossless source, DSF (D64) has better characteristics.
If we consider 24-bit WAV format as qualitative source, it better DSF (D64) but worse DSF (D128).
If we can consider 32-bit float WAV as qualitative source it is the best format among compared ones.
Quality of Audio Formats by Results These Tests
(first place is best)
1. WAV PCM 32-bit float
2. DSF D128
3. WAV PCM 24-bit
4. DSF D64
5. WAV PCM 16-bit
Read more
- DSF file format. DSF extension >
- How to playback DSF files in Foobar2000 [Step-by-Step] >
- DSD vs DSF vs DFF Files Audio >
- DSF to PCM converter >
- DSF File Converter >
- DSF oversampling. D64 vs. D128 >
- Audio Converter DSF to FLAC >
Audio Basis - articles about audio