
Do you want to experience the joy of enhanced sound with your current music equipment? Are you familiar with the quality but craving more? Explore potential ways to enhance your sound without new purchases, and discover how simple tweaks might lead to better audio quality. Continue reading for valuable insights.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.
![video: How to improve sound quality [Your Guide]](jpg/sd--nk1n7im1vky.jpg)
In addition to the equipment, you have multiple recordings in geterogenous audio resolutions. But what resolution is the best for listening to music on your equipment? Below you'll find guide how to look for audio-quality improvement.
In this article, the quality may be improved via playback-distortion decreasing. One of places, where we can do it, is the analog output of digital-to-analog converter.
Resolution is combination of bit depth and sampling rate. Read below how to try to decrease the distortions for your audio equipment or portable device (digital audio player, mobile phone, etc.).
Disclaimer: Efficiency of the sound quality improvement, that described in the guideline, depends on used playback hardware and software. Sound quality improvement isn't guaranteed.
Audio system and playback sound quality
All components of audio system impact to playback sound quality. Here you can see list of the equipment itmes that impact to the quality:
- Listening room,
- Speakers,
- Amplifier,
- Digital-to-analog converter (DAC),
- Playback software,
- Resolution, format and distortion level in recordings (audio files, disks and other mediums).
Each electronic device, loudspeakers and the room cause distortions.
The speakers works together with the listening room. A room is capable to "kill sound".
When you purchase a device or loudspeaker, it should cause minimum distortions. Loudspeakers and amplifier should work at optimal loudness that correlates with the room size. Also, speaker size also defined by the room volume.
Read how to how to perform acoustic treatment...
Recording resolution work only together with DAC. Below we'll consider it.
Back to topResampling and sound quality
Digital-to-analog converter (DAC) is audio hardware that may have different distortion levels for various modes. In the article, DAC mode means a combination of sample rate, bit depth, PCM/DSD.

One or several modes may have minimal distortions. Below such mode is called "the best sounding mode".
Audio file resolution may be converted to values (sample rate, bit depth, PCM/DSD) of "the best sounding mode" to improve playback sound quality (optimization of audio files).
Read below about:
- dithering, audio resolution conversion software, and
- a step-by-step guide on how to check your audio system abilities. Probably it will help to improve the system's sound.
Example:
DAC can be able to provide lesser distortions for mode 192 kHz/24 bit/PCM than for 96 kHz/24 bit/PCM.
Therefore, the conversion of audio file resolution to 192 kHz/24 bit/PCM is recommended for playback at the DAC.
Theoretically, a higher sample rate and bit depth cause lesser noise/distortion level. However, it is an implementation matter rather.
"The best sounding mode" may be found via measurements of the test signals (see in the picture above). However, it demands precise measurement equipment and skills in the measurements.
The article describes step-by-step how to found "the best sounding mode" by ears. It is not a precise way, unlike measurements. But ears allow approximate estimating of the DAC's modes at home without additional measurement equipment.
Read more:
Back to topDithering and audio quality
In contrast, audio-file resolution changing, that work together with DAC, dithering allows increasing the sound quality of an audio file itself in some cases. Because non-linear distortions of quantization, initially correlated with an audio signal, are smoothed and transformed into uncorrelated noise after dithering.
Dither can improve the sound quality of an audio file via correlated distortion decreasing

If DAC has a noise level above the quantization noise of the audio file, the dithering impact may be decreased or disappeared even. But modern DACs, as rule, have noise level below 16-bit error quantization and dithering noise. Therefore, dithering of such DAC may impact perceived sound quality.
How to listen to dithering
- To make sound check of dithering, you should choose recording fragment with low level.
- Convert this recording with and without dithering.
- To better listening, you can some increase volume of amplifier. Compare sound of this fragment in converted files with and without dithering.
WARNING: Be careful, to avoid ear damage due to high sound level pressure.
Read more:
Back to topHow audio converter software impacts to the quality
Below pro audio conversion software is suggested to convert audio files. It has low distortion noise. Theoretically, we can neglect quality losses of conversion (including non-multiple resampling) for pro class of audio converters.
However, different modes of the audio converter's resampling filters may be there, which can cause different ear perceptions due to different features:
- steepness of resampling filter's transient band,
- ringing,
- flatness of frequency response,
- phase response linearity,
- etc.
Different converters also have different features of resampling filters.
Currently, the author knows nothing about reliable results of researches on impact of resampling-filter features to sound perception.
Also, the filtration bandwidth may impact intermodulation distortions at an analog output of DAC.
Watch video about the experiment: we can hear ultrasound noise on some equipment.
Experiment with removing ultrasound upper 20 kHz ("Optimized resampling filter") during audio file conversion.

Read more:
Back to topRecommendations for audio player
For a purer experiment, audio playback software (audio player and system audio driver) should transfer digital audio data from file to DAC without changes of binary content. As example, a preferable way for audio player software is using ASIO or WASAPI output and turning the player processing off.
For hardware (devices) adjusting settings for minimal/without sound processing is recommended.
About digital acoustic correction of a listening room read below.
Read more:
Read the step-by-step guide on how to check your audio system abilities. Probably it will help you to improve the sound.

How to improve sound quality via "the best sounding mode"
Described below testing algorithm may be used for DAC, digital audio player, music server, or any audio device, that has DAC chip.
- Find several samples of audio files with different bit depth (16, 24 bit, DSF, DFF, ISO, etc.) for testing of your audio equipment.
- Launch AuI ConverteR 48x44
For sound checking, AuI ConverteR 48x44 Free may be used. Despite free version limitations, it allows estimating the abilities of audio file optimization for your equipment or device.
- Open source audio file(s) from step #1.
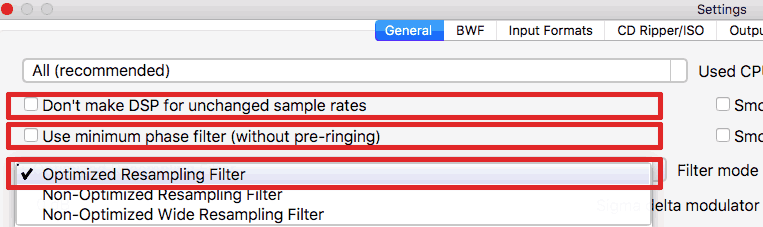
- Go to AuI ConverteR's Settings, General tab.
- Uncheck "Don't make DSP for unchanged sample rates" switch.
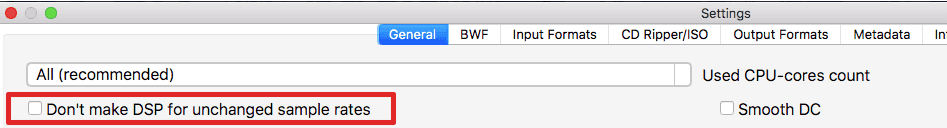
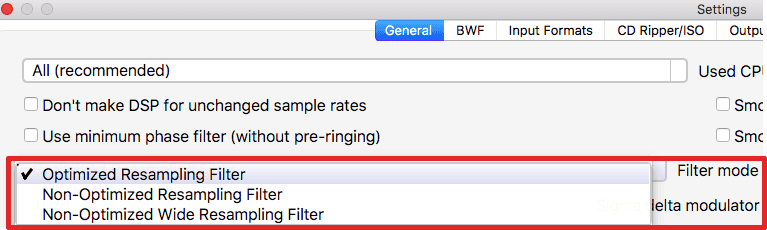
- In Filter Mode list select "Optimized resampling filter" (read about filter modes).
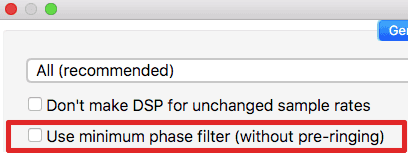
- Uncheck "Use minimum phase filter (without pre-ringing)" switch.
Minimum-phase filter causes post-ringing only (no pre-ringing). But, approximately, the energy of the post-ringing is doubled comparing post-ringing of linear (not minimum) phase filter, which causes both pre- and post-ringing.
- Click OK button.
- Select one of output format: WAV, FLAC, AIFF. If DAC supports DSD mode only, go to step #19.
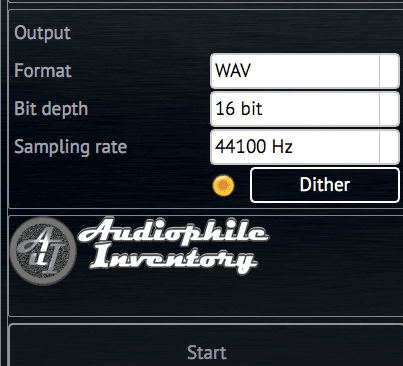
- Select output sample rate, bit depth.
Recommended to begin for maximal sample rate and bit depth, which are native to your DAC.
However, a higher sample rate and/or bit depth don't guarantee better sound quality.
- In AuI ConverteR's main window set parameters On.
For both input and output bit depth upper 16-bit "Dither" button will be ignored.
- Select new target directory
Advice: use special name directory for recognizing parameters of used conversion for further testing.
Example: "44100-16bit-DthOn", "DSD64-DthOn", etc.
- Push Start button and wait for the end of conversion.
- In the main window set Dither Off.
- Select new target directory.
- Push Start button and wait for the conversion end.
- Repeat steps #10 ... 16 for all available sample rate and bit depth combinations, that are available for your DAC or device.
- Repeat steps #10 ... 17 for all filter modes (Settings > General > Filter Mode).
For "Optimized resampling filter" test both checked and unchecked "Use minimum phase filter (without pre-ringing)" switch.
For other filter modes, this switch is ignored.
- If your DAC support DSD mode, repeat steps #10 ... 18 for output format DSF.
- Listen and compare similar files for all conversion modes: compare files with similar audio content, that are placed in the different target directories (see steps #12 and #15).
Conversion parameters of converted audio files, that have the most preferable sound, you may use for conversion (optimization) of your library to playback on tested DAC.
In general, for the DAC mode comparison, the author recommends turning off digital room acoustic correction. But you can compare results with the room correction and without.
Back to topResampling filter modes
AuI ConverteR has 3 resampling filter modes (Settings > General > Filter Mode):
- Optimized;
- Non-optimized;
- Non-optimized wide;
- Optimized G5 (since version 11.x).
click to enlarge
Optimized filter
Optimized filter cut ultrasound (all above 20 kHz).
Non-optimized filter [traditional]
Non-optimized filter:
- for PCM signals, cut half of minimum sampling rate between input and output;
- for DSD signals, cut all above 20...27 kHz depending on input sampling rate (always lesser half of minimum sampling rate between input and output ones).
Non-optimized wide filter
Non-optimized wide filter:
- for PCM signals, cut half of minimum sampling rate between input and output;
- for DSD signals, cut all above 20...100 kHz depending on input sampling rate (always lesser half of minimum sampling rate between input and output ones).
Optimized G5 filter
Optimized G5 filter cuts ultrasound (all above 20 kHz) and causes shorter ringing length for given threshold than Optimized one. G5 filter is slower other filters.
Optimized G5 transpose 440 to 432 Hz filter
Optimized G5 filter cuts ultrasound (all above 20 kHz) and transpose 440-Hz pitch to 432-Hz one. G5 filter is slower other filters. Read details...
Our recommendations for the filter using:
- Optimized mode is common recommended for better sound quality of playback.
- However, you can use any mode, that you like more. Refer to your personal listening experience.
- If non-optimized mode causes noise at specific software+hardware, try optimized mode.
- If you distribute converted recordings, non-optimized mode for PCM may be recommended. For DSD files, either non-optimized or non-optimized wide mode may be recommended.
If you use optimized mode, the distributed recording may looks like conversion from CD. Despite it is not the same, your customers may have doubts in source of the distributed hi-res recordings, and additional explanation is need.
Tips
- If Settings > General > "Don't make DSP..." switch is checked and no audio processing (resampling, gain, DSD to/from PCM, etc.) is applied, resampling filter is ignored.
- Filters are calibrated for maximum level of seep sines, but big spectrum energy of musical signal can cause distortions. So, reducing of output level at 0.4 ... 3 dB may be recommended when distortions are happen.
Back to top
Conclusions
If optimization of audio files gives audible sound advantages in your case, you can convert your audio library to "the best sounding mode"'s parameters: sample rate, bit depth, DSD/PCM.
If in your case no audible sound advantages by optimization, there is not necessary to optimize your library.
It is strongly recommended, original audio files are backup. Because you, probably, will buy new devices or/and new resolution conversion algorithms will be released.
Back to topFrequently Asked Questions
What is meant by sound quality?
Sound quality is сlarity of sound. Read details...
How can I improve sound quality?
To improve sound quality you are need pay attention components of your audio system (in importance descending order):
- loudspeakers;
- DAC;
- amplifier;
- recording;
- playback and conversion sotware, its settings.
- power conditioner (optionally)
Also, read music-file optimization guide...
How do I make my audio clearer?
To make audio clearer, it's necessary to reduce distortions and noise.
Read that you can to do here...
How do I make sound clear and crisp?
In the general case, it should be done on recording and mixing stage. Though, you can try it on mix.
General concept: boosting of high frequencies, optional its parallel compressing and mixing to target audio; noise should be suppressed available way.
How do you fix a muffled sound?
Muffled sound may have different reasons. It may be partially compansated via:
- boosting of high frequencies with EQ;
- compression of dynamic range with boosting level with compressor effect;
- boosting level.
Which is best audio quality?
Audio quality is estimated 2 ways:
- how it sounds subjectively, and
- how many distortions are measured objectively.
Anyway, zero distortions is the best. But sound is not exists in the vacuum. Listening conditions does matter.
Thus, sound quality is individual criteria, that may refer to persons or their groups.
Read more...
What gives sound its quality?
In the first place, sound quality is result of low distortion level. However, some details are there.
Read more...
How can I improve MP3 sound quality?
You can't improve mp3 sound quality as itself. However, you can optimize the audio resolution of the mp3's content, when you convert it to WAV/FLAC/AIFF/ALAC//AAC/etc. this way...
Is there an app to improve sound quality?
Sound quality may be improved different ways and kinds of applications, respectively. In instance, you can use equalizer (EQ) app and boost high and/or low frequencies, compress dynamic range with compressor application, etc.
By the author opinion, music may be upsampled or downsampled with proper audio converter to optimize for sound quality abilities of your DAC. Read more...
How can I boost the sound on my computer?
- You can check out mixer on the computer and make maximum gain.
- Also, you can install special software. Look at a search engine "real time boost volume windows" or "real time boost volume mac".
- What is optimization audio for DAC [Article] >
- R2R Ladder DAC vs Sigma-Delta DAC vs DSD DAC >
- NOS DAC. Non-Oversampling DAC [Advantages, Disadvantages] >
- DSF File Format. Quality issues [Article] >
- DFF File Format [Article] >
- FLAC File Format. Quality issues [Article] >
- Where is the Limit of Audio Quality? [Article] >
- True Gapless Conversion (seamless album conversion for operas, live concerts, etc.) >
- 7 Keystones of Accurate HiFi Blind Test [Article] >
Back to top