Audio Basis - articles about audio
Downsampling is a kind of sample rate conversion that is dividing frequency. Sometimes, it's a decimation of samples. Read how to downsampling works.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.

Why is downsampling needed?
As rule, downsampling is needed for adapting audio files for available devices and software.
Read also about sound quality optimization for DAC...
Back to topHow do you downsample music?
You can downsample music with sample rate converter software.
You can downsample music this way:
- Start sample rate converter software AuI ConverteR 48x44.
- In the main window, push Open files button. In the open file windows, select audio files in PCM or DSD format.
- In the right of the main window, in the Format panel, select audio format (WAV, FLAC, etc.), bit depth, and sample rate what you want to get.
- In the main window (left lower part), Directory output files field, select directory, where output files will placed.
- Click Start button.
- Wait until the conversion is finished. Look for converted files in the directory that is selected in goal 4.
Read more...
Back to topHow downsampling works
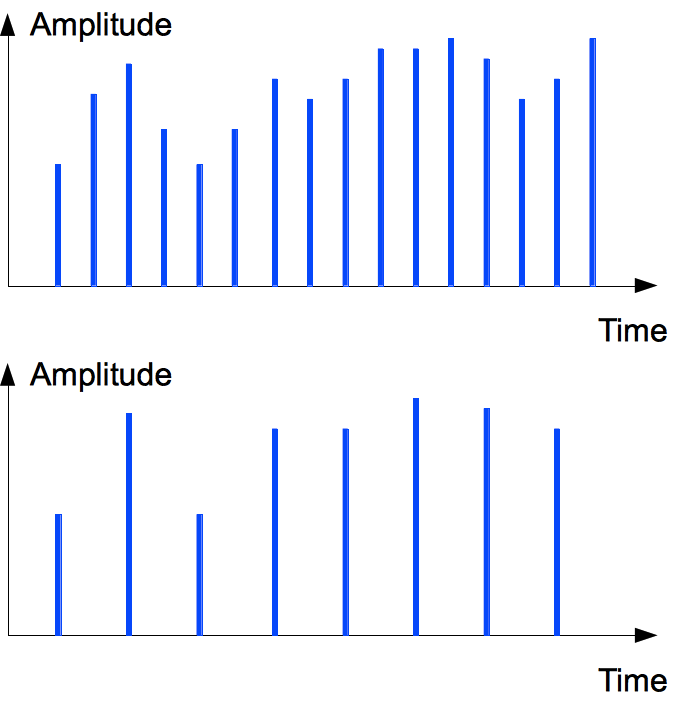
How to divide sample frequency (downsampling) two times? Every second sample of the source signal is simply removed.
Alternatively, downsampling may be done via interpolation. It may be done for non-multiple changing of the sample rate.
However, some non-multiple resampling types are provided via multiplying and dividing to integer values.
Read details...
Back to top
Sound quality
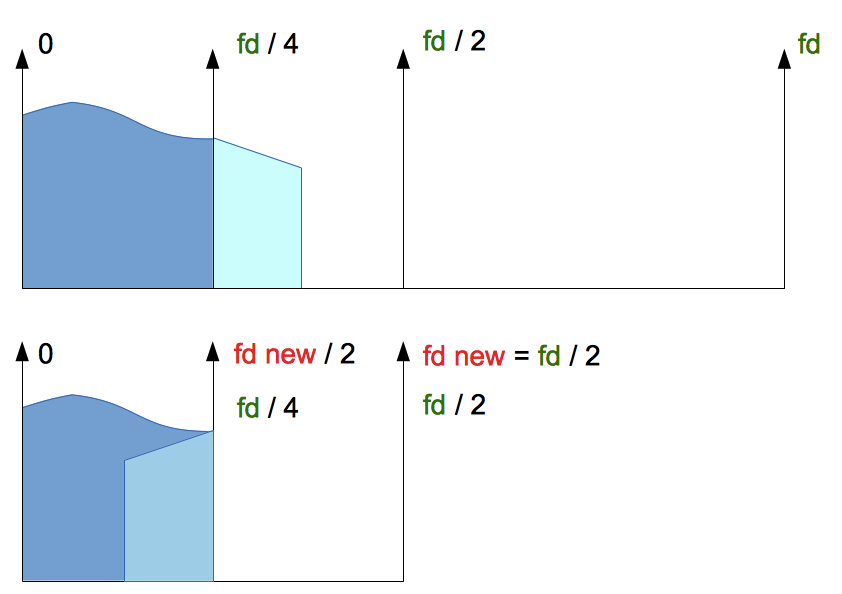
The output spectrum is shown at the bottom of the picture.
The light blue area of the source spectrum is "folded" on the spectrum of audio with a divided sampling rate.
It is non-linear distortions that arise in useful spectrum band after sampling rate dividing.
Spectrum audio after downsampling
On top of the picture, we can see the spectrum of the source audio signal with sampling rate fd. Source signal's spectrum consists of 2 areas (blue and light blue). We see light blue is placed above fd/4.
We divide 2-times the sample rate of source audio and watch to metamorphoses of its spectrum. New sample rate is fd new = fd / 2.
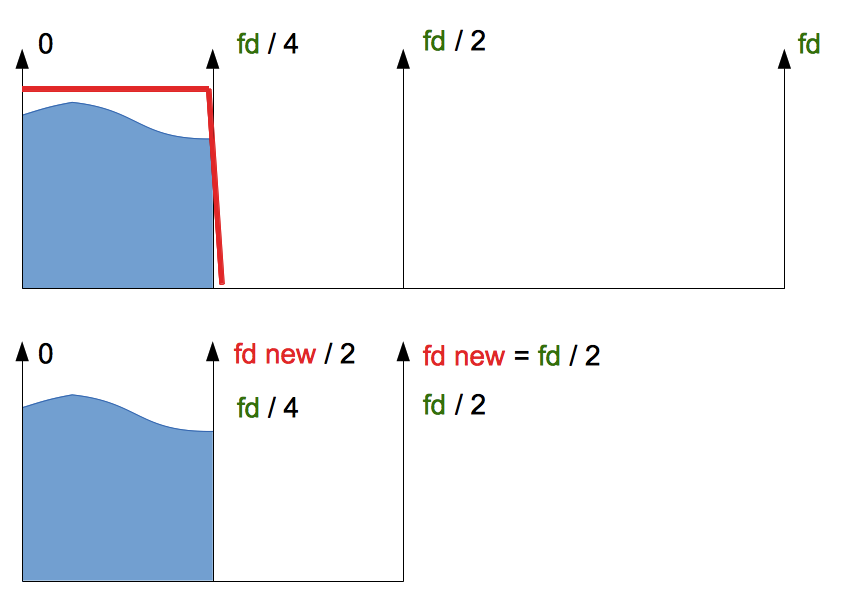
Can this be avoided?
Yes. Before dividing we need to filter (suppress) the source spectrum above fd new / 2 = fd / 4.
About oversampling read here...
Frequently Asked Questions
What is downsampling in audio?
Downsampling in audio is reducing of the sampling rate of an audio stream/file. Read more...
Does sample rate conversion affect sound quality?
Sample rate conversion may affect to sound quality. If the processing is not qualitative, it can cause distortions.
Also, sample rate may impact to playback distortions of a digital-to-analog converter.
Read more...
Does downsampling reduce audio quality?
Downsampling loses some information of audio due to lost sampling rate difference. If the target sampling rate is above 44.1 kHz, you can don't worry about the audible range.
A proper resampling tool almost doesn't cause additional losses. Read details...
What is the effect of downsampling?
Downsampling loses sound information and it should degrade the sound.
In the case of a target band of more than 20 kHz, proper downsampling should not cause an audible effect.
But some nuances are there. Read details...
How is downsampling done?
Downsampling may be done in 2 ways: decimation or interpolation.
Read details...
- What is PCM audio >
- Audio Sample Rate Converter >
- Oversampling >
- DSF oversampling. D64 vs. D128 >
- What Better Multiple or Non-Multiple Resampling >
- Would need sample rates 352 and 384 kHz >
Back to top