Audio Basis - articles about audio
Resampling (upsampling, downsampling, oversampling) is a sample rate altering of an audio stream or file.
Standard audio sample rates are based on 44.1 and 48 kHz.
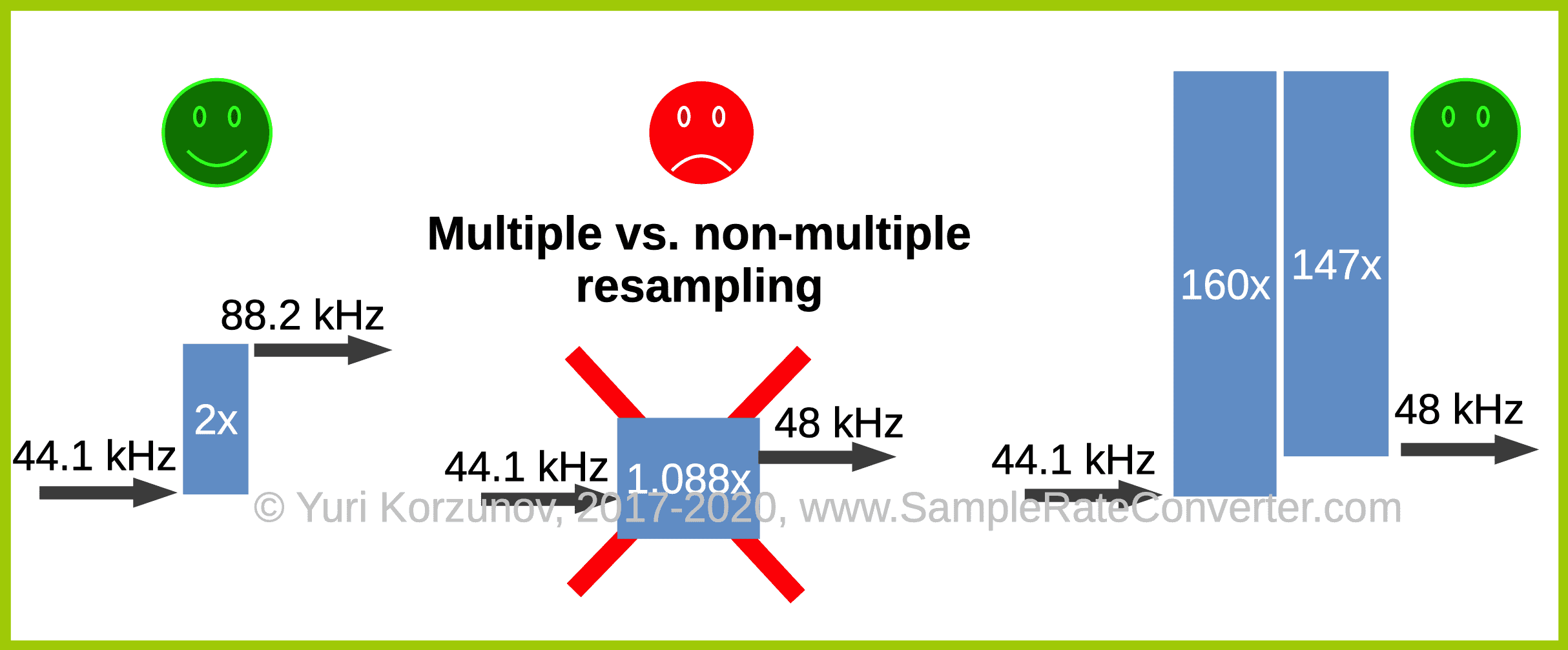
Somebody thinks that multiple resampling (integer sampling rate multiplication/division) have lesser distortions than non-multiple one. Read below about the difference between both resampling kinds.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.

Back to top
What is audio resampling?
Digital audio signal consists of sequence of instant values of audio waveform. These valuses are called "samples".
Number samples per second is called "sample rate".
Altering of sample rate is called "resampling".

How resampling works
Resampling may be performed via audio sample rate converter software (Mac, Windows and Linux Wine).
The altering may be real-time or offline.
As rule, it's used for adjusting sound files to compatibility or optimal playback for DAC. Read more >
Upsampling
Upsampling is is sample rate (sampling frequency) increasing. It includes multiple and non-multiple sampling-rate changing.
Any altering of sampling frequency may be done via interpolation between samples of source signal.
Interpolation here is a reconstruction of absent parts of waveform of digital signal
Digital signal consists of samples. Sample is an instant value of waveform in given time. Samples exist in some time moments. Between these moments wave form's time values are unknown.
Interpolation gets known sample values and builds sample values between existing ones.
But other methods are there.
How it works we will consider below.
versampling
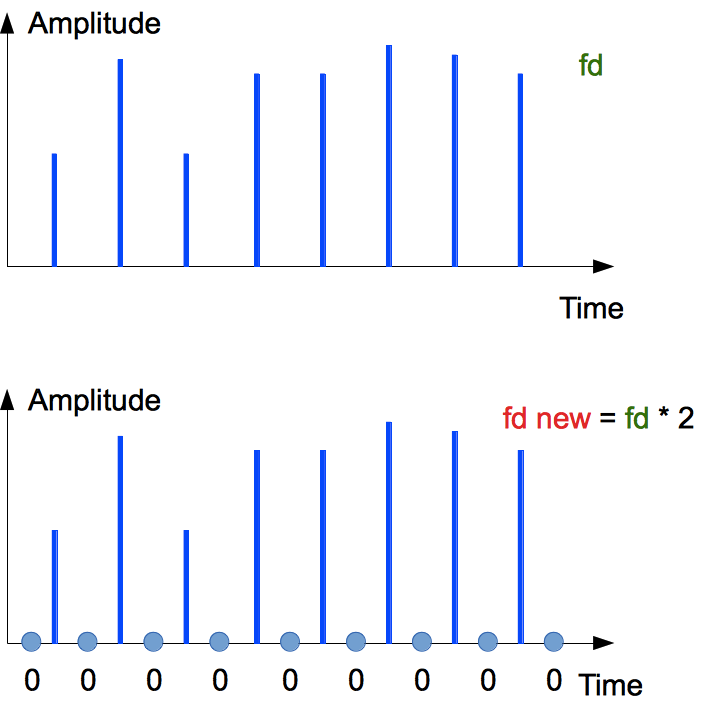
Oversampling is multiple upsampling.
Multiple upsampling is provided by adding "virtual" samples between the original signal's ones.
Upsampling audio
These samples can be added via an interpolator. The interpolator can be implemented as spline function, which can cause harmonic distortions.
Spline interpolation is like a steel-edge ruler that is fixed in points of real point sample values.
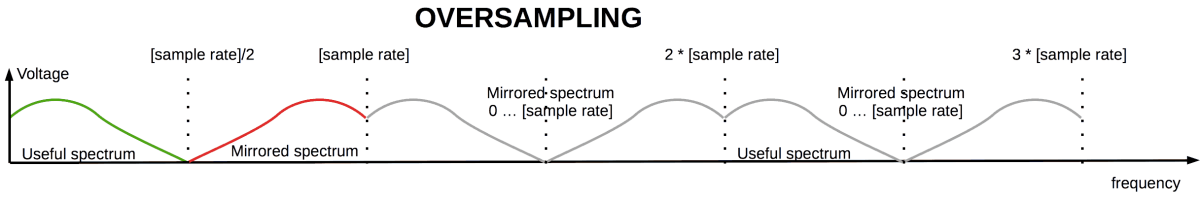
But in the audio resampling zero-level samples are inserted as "virtual". However, it distorts musical signal. Aliases are risen. And, the spectrum is periodically mirrored along the range above Nyquist frequency (half of discretization frequency).
Oversampled musical record spectrum
To keep the initial spectrum the aliases are eliminated by a digital filter. Digital filtration causes ringing artifacts. It's some small oscillations of amplitude-frequency response. If minimum-phase filter is used, its phase-frequency response is non-linear.
Multiple upsampler audio
Low-frequency filter work at frequency [input sample rate] x [oversampling coefficient].
Low-frequency filtering should cut all frequencies above half of minimum sample rate (input or output).
Example:
If input 44100 Hz and output 88200 Hz, filter cuts frequency is 22050 Hz = 44100/2
Low-frequency filtration work at 88200 Hz = 44100 x 2.
In general, non-multiple upsampling is implemented via interpolator only.
But for frequencies 44.1 kHz and 48 kHz integer coefficients 160 and 147 exist:
44100 Hz * 160 / 147 = 48000 Hz
44100 Hz * 320 / 147 = 96000 Hz
etc.
Non-multiple upsampling
Example:
If input 44100 Hz and output 48000 Hz, filter cut frequency is 22050 Hz = 44100/2
Low-frequency filtering work at 7056000 Hz = 44100 x 160.
Implementation of multiple and non-multiple resampling for standard audio sample rates may be different.
Read more...
Decimation
Decimation is a multiple sample rate decreasing.
Multiple downsampling is applied via decimation.
Decimation is a removing samples between the ones at the filter input.
Multiple downsampling
Demands to filtering like oversampling.
Downsampling
Downsampling is multiple and non-multiple sample rate decreasing.
Non-multiple downsampling may be implemented via interpolator.
But for sample rates based on 44.1 kHz and 48 kHz integer coefficients 160 and 147 may be applied:
48000 Hz * 147 / 160 = 44100 Hz
96000 Hz * 147 / 320 = 44100 Hz
etc.
Non-multiple downsampling
Input signal is multiple oversampled and downsampled and filtered once.
Read more...
Back to top
Conclusions
For standard sample rates, based on 44.1 kHz and 48 kHz, multiple and non-multiple resampling audio is performed the same way.
But there is a difference between digital filter's implementations is probable.
As rule, professional sample rate conversion software has the minimum difference.
For proper sample rate converter software multiple or non-multiple resampling ratio does not matter.
- Audio Sample Rate Converter >
- Oversampling >
- Downsampling >
- How oversample DSF audio file >
- DSF oversampling. D64 vs. D128 >
- What Better Multiple or Non-Multiple Resampling >
- Would need sample rates 352 and 384 kHz >
Back to top