Are you curious about the buzz around DSD audio? It's a format that challenges the norms of digital sound. Let's demystify it together.
Imagine a sound so clear, it rivals the best in digital formats. That's the promise of 1-bit DSD. It stands toe-to-toe with the usual multi-bit tracks, offering a high-fidelity experience.
Join us as we unravel the secrets of DSD. Learn how it captures the nuances of music, is it better than PCM, and where you can find this pristine audio. Plus, we'll bust some common myths along the way.
Ready to get other listening experience? Dive into the full story on our website.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.

What is DSD audio?
DSD, short for Direct Stream Digital, is a high-quality audio format loved by music enthusiasts. It turns sound waves into digital signals using a method that captures subtle details with just 1 bit per sound channel.
This format was created as a high-end alternative to PCM, the standard for CDs and digital files like WAV, FLAC, and mp3. DSD is also a trademark owned by SONY and Philips.
Back to topDSD music file formats
Originally for saving old recordings, DSD now offers studio-level sound for everyone. You can find it on SACD discs, .dsf, .dff files, and SACD ISOs for both stereo and surround sound systems.
Some albums come in a 1-bit digital format, paired with a CUE file in DSF/DFF formats.
DFF and SACD ISO files, along with discs, can be with or without DST compression.
DoP, an open protocol, wraps 1-bit audio in a multi-bit package so different devices and software can play it. But it's not the same as regular PCM audio. More on this below.
DSD audio can also be sent over networks.
The standard DSD64 format needs a bit rate of 2.8 Mbit/sec, which is calculated as 44100 Hz * 64 / 1024 / 1024.
Uncompressed DSD64 demands capacity: 2.7 Mbit/sec = 44100 Hz * 64 / 1024 / 1024.
Learn more:
Back to topHow can I play DSD?
To listen to DSD audio, you can use a smartphone, computer, media server, SACD player, or a specialized audio player.
SACD discs are typically played on dedicated players. Consumer computers haven't SACD drives for playing or recording these discs. SACD discs can be ripped to SACD ISO files.
For stereo systems, multichannel audio can be mixed down to two channels. This process, known as downmixing, conserves space but may reduce audio quality depending on how it's done.
Some gadgets and apps can directly play DSD files on digital-to-analog converters (DACs) designed for DSD.
Playing 1-bit audio on Windows might require a specific ASIO driver that uses the DSD over PCM (DoP) protocol, which we'll explore further.
The quality of sound is influenced by the original recording, as well as the playback hardware and software.
Can you play DSD without a DAC?
You can listen to DSD with a standard digital-to-analog converter. Some DSD players can convert DSD audio for these DACs on the fly.
Or, you can change DSD into PCM format using software for broader compatibility.
See more:
Back to topWhere can I get DSD music in files and SACD?
You can buy Direct Stream Digital music in online stores as DSD file downloads or SACD disks with physical delivery.
- Go to free DSD download sites...
- Listen to the audio samples for free...
- See DSD online stores...
Back to top
How to convert DSD?
How rip DSD from SACD to SACD ISO read in the guide...
Read how to convert DSD to FLAC...

How to convert to playback at iTunes?
To listen DSD on iTunes, convert:
Does conversion DSD to multibit format degrade sound?
When convert with audio processing (including Direct Stream Digital to Pulse Code Modulation), it's not lossless technically. But final quality is a matter of used conversion software and playback setup. Read details
Do various DSD converters have different sound quality?
Yes. There is a different distortion level and tolerance to overload. Read details here.
Back to top
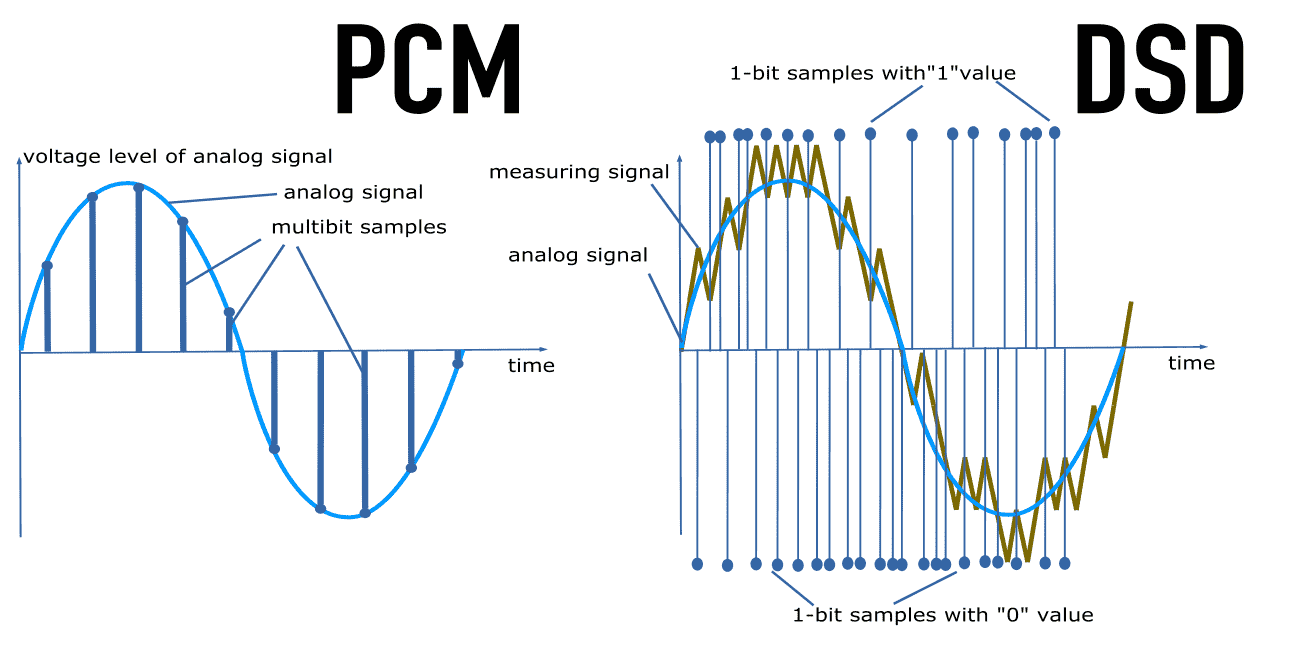
DSD vs PCM
An audio signal is an air oscillation (sound) converted to electrical oscillations via a microphone.
Digital form of an electrical audio signal is a number sequence that is converted in analog-t-digital converter (ADC).
The sequence allows the creation of electrical oscillations back via digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
An audio signal (the electrical oscillations) may be presented in Direct Stream Digital or Pulse Code Modulation.
It’s like we can assemble the same mosaic from small squares or circles.
Below we’ll return to the metaphor.
What is the difference between Direct Stream Digital and Pulse Code Modulation?
Both onebit and multibit streams are a sequence of measured values (samples) of an audio signal's oscillation.
Sound/air oscillation each moment has a certain position (instant pressure level). The pressure level after the microphone is converted to an electrical oscillation.
The electrical oscillation at each moment has a certain position that refers to the air pressure level.
Pulse Code Modulation consists of samples. The sample is a measurement (number value) of an instant position of the electrical oscillation (voltage) at the moment of the measurement.
1 sample = 1 instant measurement of the voltage.
The voltage level at the microphone input is measured over equal time.
In sigma-delta modulation (a.k.a. DSD) each 1-bit sample shows a positive [1] or negative [0] change of the pressure level relatively to its previous value.
And, as rule, the sigma-delta modulation is explained as a saw (level grows or falls) between samples. But, it does not give an easy understanding of the basic DSD principle.
Below we'll consider the easier explanation. Keep reading.
Study articles:
Back to topDSD music production: record, edit, mixing, mastering
Is native DSD editing possible?
Audio editing is cutting, merging, gain altering, equalizing, etc. of file(s).
"Native editing" (without conversion to multibit and DSD re-modulation) is possible for cutting and merging onebit records in bit-perfect mode only.
All other kinds of editing demand conversion to multi-bit values and re-modulation. In this case, losses of the editing are comparable with multibit resampling.
Mixing, mastering
For DSD recording, dedicated audio interfaces are used.
Pulse Code Modulation here may be considered as "multibit DSD". Pulse Code Modulation is not obligatory to mean "24 bit / 352 kHz" or so on. Author recommends use 32- or 64-bit float point bit depth. This PCM contains high-frequency modulation products. They are excessive. But, for conversion of this "multibit DSD" to 1-bit one, re-modulation is required.
Losses of editing with 1-bit/multibit conversion are comparable with resampling.
Thus, audio tracks in 1-bit format should be converted to PCM audio (filtered or DXD). After it them are mixed and mastered. Final mix is modulated to DSD back.
Recording studios may distribute 1-bit records without editing. These recording are once captured from microphones.
Study details here >
Back to topDSD history and development
Audio CD optical disk (Pulse Code Modulation format) was one of the first digital formats. It was a source with low distortion level in comparison analog recordings. I think, now many people forgot what is "real analog hum".

After CD, demands to sound quality improvements could be implemented by increasing sample rate or bit depth.
Audio quality (sound quality) is a level of distortions, that format/software/equipment causes. The level may be normalized by psychoacoustic criteria.
However, Sony and Phillips decided to use another kind of modulation - 1-bit sigma-delta modulation. At the first glance, using 1-bit is impossible, because such bit depth (resolution) causes a huge noise level. But, if high sample rates are used, the noise energy may be pushed out of the audible frequency range (to ultrasound). That action is called "noise shaping".
Practically, 1-bit conception may be easier, than multi-bit, in a DAC implementation (read below).
When DSD music is converted to analog, ultrasound useless content is filtered.
Medium, which contains 1-bit DSD audio stream was called SACD (Super Audio CD).
Modern DSD gets higher sampling rates: DSD128, DSD256, DSD512, DSD1024.
It allows solving some technical issues that are described below.
Look at DSD file infographic >
Back to topDSD specification
| Abbreviation of: | Direct Stream Digital |
|---|---|
| Audio data coding method: | sigma-delta modulation (details and video) |
| Bit depth: | 1 bit or more (details about sound quality) |
| Sample rate: | DSD64 (2.8 MHz), DSD128 (5.6 MHz, double), DSD256 (11.2 MHz, quad), etc. (details) |
| Channel number: | Stereo or multichannel |
| Medium: | SACD optical disk, including hybrid SACD (with CD layer), computer files [SACD ISO (ripped albums from SACD) and DSF, DFF, CUE+DSF/DFF] (details) |
| Specification: | "Scarlet book" (1999) |
| Applications: | Music production, home hi-fi/hi-end audio |
Direct Stream Digital is one of high-resolution audio formats to improve CD-audio dynamic range in the audible band.
See below about sound quality issues (distortions, bit depth, band, sample rate, Direct Stream Digital versus Pulse Code Modulation).
How DSD works?
DSD encoding
Multibit signal is like to a computer display. It consists of several pixels along both X and Y axis.
XXXXX
XXXXX
XXXXX
DSD looks like a 1-pixel screen.
X
And we can't understand: how a 1-pixel display is capable to show a qualitative picture?
Imagine that, this one pixel is put on a truck. And the truck moves the pixel sequentially through all locations of multiple pixels of the first display. The movement is cyclic.
X . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. X . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . X . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
And it moves very-very quickly. And so rapid movement allows us to see high qualitative picture.
As rule, DSD has been explained in the time domain: positive samples increase level, and, negative sample decreases. After it, analog filter smooths "saw" form of signal.
In DSD analog-to-digital converter (ADC), measuring the "saw" signal is compared with the input analog signal.
At the ADC output "1" is present. And measuring-signal level grows until it exceeds the current level of the input analog signal.
It causes the output signal to switch to "0". And measuring signal begins to reduce level.
When the measuring signal level is a lesser input signal of the ADC, its output is switched to "1". And measuring signal grows until the exceeding the input signal.
Learn how to sigma-delta modulator works...
Above we discussed onebit and multibit formats like a mosaic from squares and circles.
These figures may be significantly smaller than the assembled image. If our eye can't resolve the figures, there is no difference between the squares or circles we use.
So, qualitative onebit and multibit systems may bring us the same final result.
Such an explanation causes difficulties in understanding what is the actual difference between these formats and how to process Direct Stream Digital. Probably, it creates the myth about "native" DSD processing. About the processing see below in "DSD editing software" part.
Instead of the explanation, in the author's opinion, the easiest way to understand how DSD works is its spectrum consideration.
To estimate DSD and PCM sound quality, the quantization-noise level is the main criterion.
There is an explanation, that DSD has a super high sample rate and, thus, super low bit depth 1-bit does not matter for noise.
But DSD 64 sampling rate (2,8 MHz = 44.1 kHz * 64) is not enough to be better CD audio (study details).
To decrease noise level, noise shaping is used.
1-bit quantization-error (noise) energy has a significant level.
However, there is, so-called noise shaping of the spectrum is used. And quantization-error energy is re-distributed.
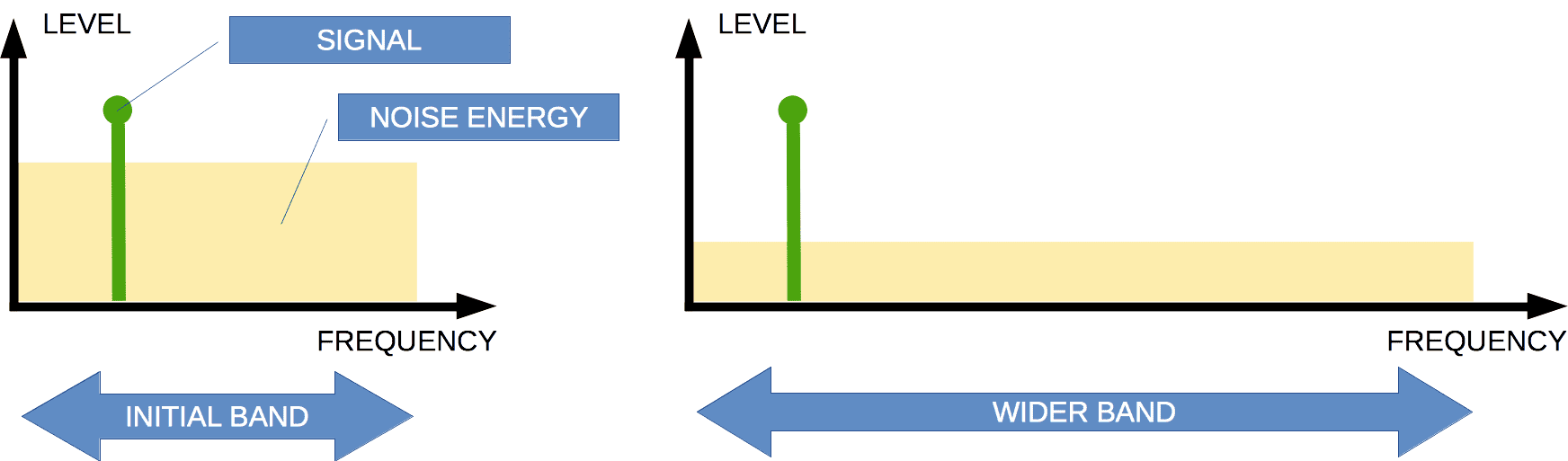
Noise shaping (NS) of 1-bit signal (spectrum)
Noise shaping in the simple words
Let's imagine noise energy as water in a pool.
If we blow strongly to the water surface at one poolside, water level of this side is decreased (noise is decreased in audible range).
It is the same adding more bits of audio resolution.
The water will be displaced to the other poolside (inaudible ultrasound range). And level there grow.
The quantization-distortion spectrum (at the left of the picture) has a level comparable with a musical signal. The sigma-delta modulator pushes a significant part of the energy from the low- to high-frequency range, out of the audible band (0 ... 20 kHz).
Noise shaping is implemented in a sigma-delta modulator (a.k.a. DSD modulator).
What is DSD decoding?
When the 1-bit record is played back, a low-frequency filter into a sigma-delta demodulator (a.k.a. DSD demodulator, DSD decoder) cut all excessive sound information.
DSD decoder (demodulator)
Spectrum error is noise level.
Therefore, DSD error into the audible range is comparable with the error of multi-bit pulse code modulation.
Also, sigma-delta modulation may have a multi-bit resolution. Read the details below and watch the video on this page.
Back to topSample rates
The format uses standard range of sample rates based on 44100 Hz:
- DSD64 = 44100 * 64 = 2'822'400 Hz = 2.8 MHz
- DSD128 = 44100 * 128 = 5'644'800 Hz = 5.6 MHz
- DSD256 = 44100 * 256 = 11'289'600 Hz = 11.3 MHz
- DSD512 = 44100 * 512 = 22'579'200 Hz = 22.6 MHz
- DSD1024 = 44100 * 1024 = 45'158'400 Hz = 45.2 MHz
- Etc.
Also, 48000-kHz base is possible. There are no technical limitations to the sample rate value. But hardware/software compatibility issues are very probable.
Back to topDSD and Nyquist Theorem
For the Nyquist theorem no difference between Direct Stream Digital (sigma-delta modulation) and Pulse Code Modulation:
the spectrum above [sample rate]/2 is
the same as the spectrum below [sample rate]/2
that flipped along the frequency axis.
Noise, Maximal Level and Overload Stability
When a sigma-delta modulator is designed, the engineers pay attention to two main parameters:
- the distortion level in the audible range and
- tolerance to overload.
To solve these issues the engineers use:
- bit-depth,
- sample rate,
- noise shaping,
- set default output level -6 dB for the modulator.
All these parameters should be considered comprehensively.
Bit depth
Bit depth reduces the quantization error level itself.
Noise shaping
NS "pushes" a significant part of the quantization error energy out of the audible range.
We can suggest that more energy may be pushed out of the range in the sigma-delta modulator. But it requires a steeper noise shaper.
Steeper NS is capable to cause a higher probability of glitch (broken stability) of a sigma-delta modulator when input overload happens.
After the glitch, silence or some oscillations are generated at the output of the sigma-delta modulator.
After broken stability, the modulator should be forcibly reset.
Sample rate
We remember that quantization error is noise spectrum level. It is a level of distortions.
A higher sample rate distributes the same noise-hump energy into a wider band.
It reduces the hump level or "quantization error" of Direct Stream Digital.
Also, a wider band allows using sloper noise shaping.
Energy is a square of the figure, concluded between the spectrum line and horizontal axis into band 0 ... [sample rate]/2.
In the left and right pictures, the squares of the noise energy figures are the same. But the figure, which is more expanded in the horizontal axis, gives a lower noise hump.
A higher sample rate allows for reducing the hump level in the audible frequency range. It allows for reducing noise shaping's steepness, which increases the overload tolerance of the modulator.
We can see that lower distortions and higher stability to overload may be achieved in different ways.
As an example, better quality is noise-shaping implementation matter for the same bit depth and sample rate. But, on the other hand, we can increase the sample rate and/or bit depth to decrease the error level for the same NS method. It allows for the improvement of the audio quality.
Back to top
DSD in figures
Pro audio modulators have noise levels in the audible frequency range for sample rates (read details):
- D64 about -125 ... -145 dB (comparable with 24-bit)
- D128 about -165 dB (better than 24-bit)
- D256 and higher about -170 ... -200 dB (comparable with 32-bit)
Noise hump in the audible frequency band almost doesn't depend on demodulator. And, the excessive products should be maximally suppressed out of the band. Ultrasound content can cause audible intermodulation distortions.
Learn more: DSD vs DSF vs DFF >
Back to topDSD myths
Myth 1. DSD is better PCM and vice versa
No. Both format quality is defined by implementation in a device and software.
Also played back record is a matter.
Myth 2. DSD has low noise level due to high sample rate
Direct Stream Digital's low noise level is a result of noise shaping.
Myth 3. Multi-bit DSD may be edited natively
DSD bit depth defines distortion level abilities. After the editing, sigma-delta re-modulation is needed.
Study DSD editing...
Myth 4. DSD editing with decimation dramatically degrades sound
The editing with decimation is implemented with a low-frequency filter. The filter causes ringing audio.
However, the author knows no serious researche, that is studied the real impact of ringing on the listening perception.
Also, the ringing depends on filter implementation.
So, currently, we don't know the exact answer to the question.
Read about ringing audio...
Back to top
DSD vs FLAC, WAV, PCM comparison
Now we'll consider, which is better PCM or DSD?
Ability comparison
Bit depth defines audible noise. More bit depth means lesser noise.
In the picture, we can see that bit-depth decreasing is achieved by using only part of the full signal frequency band. In other words, if we want to reduce bit depth, we must increase the sample rate to keep the audible noise level.
See details of the format comparison in the table: DSD vs WAV vs PCM vs FLAC vs DXD
| Fea |
DSD | FLAC | WAV | PCM | DXD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coding | sigma-delta modula |
pulse code modula |
pulse code modula |
pulse code modula |
pulse code modula |
| Samp |
44100 x 64 x N | up to 384'000 Hz | up to 2'147'483'648 Hz | no limit | 352 / 705 kHz |
| Bit depth |
1 bit, |
16 ... 24 bit, |
16 ... 64 bit inte |
multi |
24/32 bit |
| Band for audio signal | Low part of the band | Full band | Full band | Full band | Low part of the band |
| Medium | file, optical disk: SACD | file | file | file, digital tape, optical disk: CD, DVD |
Note: WAV and FLAC are PCM format implementations.
Read which is better DSD or FLAC (Infographic) >
Study more audio file formats >
Direct Stream Digital (sigma-delta modulation) is like to pulse code modulation, but quantization error spectrum is shaped for decreasing noise into the audible range.
We may apply the noise shaping for usual Pulse Code Modulation. But the difference here is band reserve for pushed noise out of audible frequency range.
PCM has a lesser band reserve (above audible range) than sigma-delta modulation format, but pulse code modulation has higher bit depth.
Noise shaping for pulse-code modulation is an implementation matter too, like sigma-delta modulation.
Therefore, no format advantages as itself. But implementation makes a difference.
Sigma-delta-modulation decoder (demodulator) is 2-position (1 / -1) voltage generator and low-frequency filter. It is simpler than pulse-code-modulation hardware demodulator. Because pulse-code demodulator contains multi-voltage matrix or 1-bit decoder(s). So we have more abilities to make cheaper 1-bit DAC better than multi-bit one.
Learn details here >
Also, look at infographic DSD versus FLAC >
PCM vs DSD sound quality
There is no univocal answer. There are several reasons:
- Quality of a record
- Mixing/re-mixing of the record (including quality of the processing)
- Playback software/hardware implementation
- DAC implementation.
These reasons trigger infinite discussions about "what is better PCM or DSD".
Technically, Direct Stream Digital and Pulse Code Modulation are incomparable. Even as single multiformat digital-to-analog converter is used for the test, the difference may be caused by different mixing/post-production of records, and the DAC uses different circuits (see here).
General answer: "Each case is individual and depends on playback system implementation and listened to record".
DSD sound quality and other [brief F.A.Q.]
Are DSD downloads worth it? Are DSD files better?
There is no unambiguous answer to the question. It depends on record quality, your software and equipment.
Is DSD better than FLAC?
There is no answer. Theoretically, DSD has better potential than FLAC and other multibit formats. Recording, certain equipment makes sound quality. See details...
How big are dsd files?
1 minute of DSD64 stereo is about 40 Mbytes.
See more...
Are all SACD DSD?
Yes. Hybrid SACD also may contain CD layer compatible with usual CD player.
Why is DSD sounds better than PCM?
Sound is defined by record quality, your playback program and apparatus.
Why upsample to DSD?
Upsampling can optimize audio file resolution to optimal (minimal playback distortions) for your equipment. Read details >
PCM versus DSD ADC
Both kinds of DAC contain sigma-delta modulator. It converts the analog voltage to digital samples in a format like Direct Stream Digital.
Analog filter ["DSD" sample rate]/2 is applied before the modulator. Looks details here...
PCM ADC is more sophisticated and contains a multibit modulator.
To reduce the sample rate, the "multibit-DSD" signal should be filtered (low-frequency filter) and decimated (removing part of samples). The filter also eliminates the shaped noise of the "DSD signal".
Read more about the format difference...
Back to top
PCM versus DSD DAC
To easier providing of multibit DAC precision/linearity in this kind of DAC, a digital sigma-delta modulator is used. After it, sigma-delta de-modulator converts digital "DSD" to an analog signal.
In the general case, DSD DAC is simpler. It contains sigma-delta de-modulator only.
It is technically impossible to compare multibit and DSD DACs, because they use different processing / electrical circuits.
Study more: what is DSD and PCM DACs and their comparison >
Back to topWhat is DXD?
DXD is Pulse Code Modulation (as rule "24 bit / 352 kHz" or so on) with high sample rate and bit depth and legacy DSD noise hump. However, it can cause audible intermodulation distortions.
Only low part of the DXD spectrum contains useful musical signal. Noise level is growing to higher frequencies. Before non-linear processing, this high-frequency hump cutting is recommended.
As rule, the format has sample rates 352 800 Hz and above and 24-bit and above resolution.
Primarily, DXD format is intended to edit DSD.
However, there are PCM lossless formats that may be used like DXD.
Read DSD editing details...
However, not all PCM files with such sample rates are DXD. Traditional Pulse Code Modulation has no significant noise level at high frequencies.
Playback devices can filter high-frequency noise to save dynamic range and avoid intermodulation distortions.
More about DXD see here.

Is DXD better than DSD?
DXD is pulse-code-modulated sound format with noise hump in high frequencies. DSD DAC is simpler than PCM one in theory. From DAC point of view, DSD is ideal format. But, actual result is refer to digital-to-analog converter model. Read details here...
Back to topWhat is DoP (DSD over PCM)?
There are compatibility and other issues of tranfer 1-bit and multibit audio data from computer to PCM or DSD DAC.
All audio interfaces (USB, in instance) are designed for multibit data. And 1-bit data packing into ordinary multibit value was suggested.
DoP (DSD over PCM) is a format providing compatibility with some DSD hardware (USB DAC, for example). The format allows packing 1-bit DSD data in usual multi-bit words (like PCM).
These multibit packed DSD words are transferred as ordinary audio signal. Upper bits of the multi-bit word contain special "DSD over PCM" marker code.
DoP receiver should recognize the marker code and interpret lower part of the multi-bit word as raw DSD bits.
DoP format may be stored into usual lossless multibit file: WAV, FLAC, AIFF.
DoP coding may be chosen in audio player settings.
Back to top
Conclusions

- DSD (SACD) appear as improvement of CD-audio.
- Sound quality is not matter of bit number of format, but depend on implementation and quality of a musical record.
- "Native" DSD editing is possible for limited cases. For other cases, the own editing loses is comparable with PCM resampling.
DSD is onebit audio data (sigma-delta modulation) format for hi-fi audio.
For the same sample rate and bit depth, the format may have different quality, that depends on implementation.
DSD digital-to-analog converter is simpler than the multibit one. It allows getting the better quality simpler way.
DSD may be edited via 1-bit to multibit and back conversion. The edition is lossy, except merging/dividing.
Back to topFrequently Asked Questions [general]
Is DSD the same as SACD?
SACD is optical disk that contains digital audio data in DSD format. Read more...
What is DSD in DoP format?
DoP format is protocol for audio unit interaction. The protocol contains DSD audio data. Read details...
How common is DSD?
DSD is well known audiophile format. It allows achieving high sound quality and often used for classic and jazz music recording.
Read more...
What is the best audio quality?
The best audio quality has 2 definitions:
- most low distortions, or
- most"nice" sound.
When correct scientific approach is applied, both definitions may be used.
Read more...
What is the highest quality audio file?
One-bit and multibit lossless files are the highest-quality audio files. Read details here...
Is DSD better than 24 bit?
Bit depth of Direct Stream Digital and Pulse Code Modulation may be compared by quantization distortion level in the audible band. However, equipment and software play big role there. See approximate comparison of the bit depths...
Is CD better than FLAC?
FLAC format supports high-resolution audio. It give technical abilities to better sound quality.
Read details here...
What is DSD and FLAC?
DSD is family of high-resolution audio formats. FLAC is one of multibit audio formats.
Study details...
Is DSD better than mp3?
DSD is lossless audiophile format. mp3 is lossy multibit format. Also, mp3 is hi-fi format at high bitrates.
Technically, DSD is better than mp3.
Read more...
Can Windows play DSD?
You can play DSD music under Windows. Read more...
Does VLC play DSD?
As the author know, VLC player software can't play DSD files. Read the discussion...
Can you stream DSD?
DSD streaming service you can find here...
Does Spotify have DSD?
Spotify doesn't support DSD audio. Study information about DSD streaming service...
Does Qobuz stream DSD?
Qobuz does not providing DSD streaming. Check out DSD streaming service...
- DSD vs. PCM. Real competitors? What is common base? >
- DSD Decoder Audio >
- How work sigma delta modulation in audio >
- DSD Converter of Audio Files: What Inside? >
- Where to get free DSD recordings? >
- Where to buy DSD music? >
Audio Basis - articles about audio
Back to top