PCM digital-analog converter may be based on either a resistor matrix (binary weighted, R2R ladder) or a sigma-delta modulator (SDM). The last one is the most popular. But some people prefer R-2R converters. Also, non-oversampling [NOS DAC] is considered in the other article. DSD DAC is an alternative to PCM DAC. Read this article about the comparison of the digital-analog converter types, their advantages and disadvantages by audio software developer Yuri Korzunov.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.

R2R ladder DAC versus sigma-delta PCM DAC versus DSD DAC
Read the infographic description below
Without going into detail, there are two audio signal types: DSD and PCM.
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) is a 1-bit audiophile music format.
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) is a multi-bit format for music lovers and lo-fi applications. It's more popular than DSD.
Both formats have advantages and disadvantages. And there is no best format between them. Read more...
A DAC may natively support one or both of these signal types.
PCM DAC based on a sigma-delta modulator has 2 key advantages:
- the linearity of input/output voltage characteristic of digital to analog conversion;
- the simplicity of design and production.
R2R ladder DAC and binary-weighted-resistor digital-analog converters have non-linearity issues due to available resistor tolerance. The non-linearity cause distortions. Also, it can cause audible products by ultrasound, which degrades sound quality.
Sigma-delta modulator may be tough to design. But it is a pure digital module, which doesn't need to adjust during production. It simplifies manufacturing and decreases the cost of a digital-analog converter device.
However, resistor-matrix PCM DAC doesn't contain a sigma-delta modulator and has no overload issue.
DSD DAC has no issues with R2R non-linearity and overload tolerance. DSD recording (original or pre-converted from PCM) may be noise-shaped differently. The noise shaping may be more or less optimal for a converter's analog filter. Read details >

DAC design comparison in brief
Minimalistic resistor-matrix DAC (part A of the picture above) contains a resistor matrix. Each of the matrix resistors has a value deviation. It causes non-linearity.
Binary-weighted resistor DAC
Binary-weighted resistor DAC contains resistors with values R, 2R, 4R, ..., 2NR for each bit. Where N is a bit number.
R2R ladder DAC
R2R ladder DAC is also a subtype of a resistor-matrix DAC, that is built on resistors with two values R and 2R. In instance, 10 kOhm and 20 kOhm. It reduces component types and makes manufacturing easier and cheaper. Sound quality is defined by how a digital-to-analog converter is done rather.
The analog filter aim is alias removing by digital to analog conversion. Analog filter has gradual suppression growth with frequency increasing. And the analog filter can not deep filter all aliases. These aliases can cause audible distortions generated by ultrasound due to intermodulations.
Analog filter has minimal suppression in the low-frequency area. To suppress aliases in the low-frequency area, oversampling and digital filtering (steeper than analog filter) are used (part B of the picture above).
However, oversampling causes its own aliases. And issues are possible with the filtering of these aliases.
Read details here >
Non-linearity of the resistor matrix may be solved via a digital sigma-delta modulator (part C of the picture above). Because such modulator is a linear device. But the sigma-delta modulator has issues with broken stability due to overload.
Sigma-delta DAC
When input digital audio stream is DSD (1-bit sigma-delta modulation) instead PCM, minimalistic DSD DAC contains a pair of resistors and an analog filter (part D of the picture above).
Of course, real DACs are more complex devices, than are shown in the picture. There are matters of power supply quality, temperature stability, deviation of logical level voltage, etc. DAC concepts (A, B, C, D parts at the picture) give potential design abilities only. And they do not guarantee a better quality of certain DAC type.
Read below how to work these schemes in details.
Back to topFeature comparison: ladder, sigma-delta PCM, DSD DACs
| Features | Ladder (R2R) PCM DAC | Sigma-delta PCM DAC | DSD DAC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Way of voltage generation by code | Resistor matrix | Sigma-delta modulator | 1 level circuit |
| Multi switch of matrix elemets | Yes | No | No |
| Analog filtering of output signal | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Amount of reference voltage values | Bit number - 1 | 1 or more [if multi-bit sigma-delta modulator is there] |
1 |
| Linearity issues of digital to analog conversion | Non-linearity | Linear | Linear |
| Non-linear distortions in analog circuits | Yes | Yes | Yes |
When we consider conversion to an analog of sigma-delta modulation, 1 level may mean 2 levels actually (positive and negative).
Read the details in this article below.
Back to top
How DAC types sound
Often the author read in the discussions, that some people prefer one DAC type to others. They have practical experience in the sound quality of DAC types.
The author will not consider here record quality and different mixing/mastering issues, that also is a matter of DAC-sound estimation. Because it may be technically impossible to achieve the full identity of a single phonogram copy in different formats.
Audio-track production has several stages:
- recording;
- mixing;
- mastering;
- conversion to different formats.
How to musical test samples are produced
In the picture above only some options for producing music test samples are shown.
For some of the test samples, several stages may be excluded. Or single master-record (final stuff of music production) may be converted to different formats.
Single acoustic stuff may be recorded in 2 formats at once. There are differences in recording tools (microphones, microphone pre-amps, analog to digital converters, etc.) and their settings.
Therefore, DAC type comparison can include a comparison of audio file converter quality or recording tool difference at least.
The main technical problem of DAC-type comparison is the various inner working of the devices.
In the picture, the impact of DAC's internal modules to sound quality was shown for various converter types.
There are many variables, that need to be taken into account when digital-analog converters are compared.
As example, in ladder DACs, resistors with different tolerance may be installed. It can lead to different non-linearity and cause different sound. Even for different items of a single device model.
Another example: a PCM DAC has alias issues of the oversampler, but a competing DSD DAC contains a worse analog filter. It is possible to suggest which one of the digital-analog converters is better sounding? Probably, no.
So, it is technically impossible to compare the sound of DAC types as abstract units. But it is possible to compare the sound of real instances of digital-analog converters, despite its inner workings.
Back to topGeneral requirements for DAC
In simple, a digital-analog converter should provide:
- digital value conversion to analog voltage level with given precision,
- limited level of distortions (in 0 ... 20 kHz frequency range),
- given magnitude and phase linearity deviations of frequency responses.
Digital-analog converter schemes
Let's look at elementary resistor DAC:
The scheme contains the pair of resistors (R1 and R2) and the analog filter. Resistors define the voltage in point A. When digital "0" at the input, 0V is present at point A. When digital "1" is at the input, voltage, defined by R1 and R2, is present at point A.
Also, digital "0" may be converted to a negative value, to avoid DC bias at the analog output. Though there are ways to remove the bias.
Analog filter interpolates intermediate points between times of digital samples.
Voltage in point A (before analog filter) is:
V=[Bit #0 Voltage]/(R1+R2)*R2;
where:
- [Bit #0 Voltage] is logic levels "0" or "1";
- R1, R2 are values of resistors.
Thus voltage precision at point A depends on physical logic level precision and resistors' tolerance.
Resistor tolerance is the limit of resistance value deviation (in percents).
A resistor, as a real electronic component, has some value deviation. It causes voltage level deviation and non-linear DAC distortions if there are several bits (read below).
In multi-bit resistor DAC, additional resistors are added (1 resistor per 1 bit):
The resistors' values define the voltage level before the analog filter.
In the picture above (part A) we can see elementary binary-weighted DAC. Analog filtering at low sample rates (44100, 48000 Hz, as example) is one of the problems of the DAC. To solve the issue, a low sample rate is upsampled and digitally filtered before analog filtering (part B of the picture above). Read the details below.
How analog filter works
In the picture, the DAC analog filter (part A) spectrum before the analog filter is shown.
It is a spectrum of "stairs", that is drawn on PCM pictures usually.
Analog filter is an interpolator: math that creates a seamless signal between reference points of digital samples.
The ideal analog filter must cut the full frequency range above [sample rate]/2 to restore an original analog spectrum (see the picture below, part C).
Otherwise, aliases from this frequency range (above [sample rate]/2) can generate audible products due to non-linear distortions in DAC's electrical circuits (see the picture above, part D).
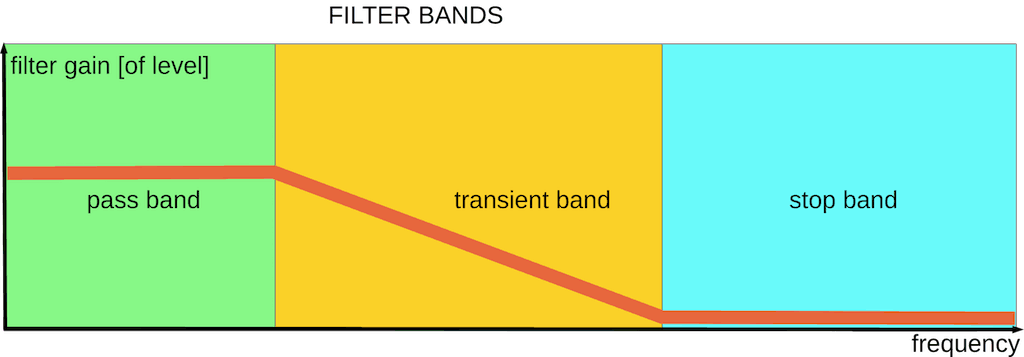
Let's look at the filter bands:
Filter bands (analog and digital): pass, transient, stop
Filter bands:
- Passband - filter pass signal thru
- Stopband - the band with maximal suppression
- Transient band - band between pass and stop bands
These bands have no exact borders. As rule bands are defined by minimal (for passband) / maximal (for stopband) allowable filter gain.
Filter gain is output/input level ratio for a given frequency.
When says "low-frequency filter" it means filter with a passband in low-frequency area.
A real analog filter is not steep and demands a wider transient band (between pass and stop bands) comparing digital filters. So it is too difficult to provide steep transient between output frequency ranges: below and above [sample rate]/2 (see picture "DAC analog filter", part C).
Thus audible products of intermodulation distortions can be caused due to the non-steep transient band of the analog filter.
To improve filtering, upsampling is implemented. It shifts the original [sample rate]/2 position ([oversampled sample rate]/2) to the area of deeper suppression of the analog filter.
Also, a digital filter, implemented in oversampling, may be steeper than an analog one.
And steeper digital filter can better remove excessive aliases, than analog filtering.
Resistor DAC non-linear distortions
When the resistors in the scheme of the resistor DAC is ideal (zero tolerance or zero resistance deviation), voltage before the analog filter is altered linearly for a sequential altering of binary code at DAC input (0000[0], 0001[1], 0010[2], 0011[3], etc.).
But errors in bit-resistor values, cause non-linearity.
Example #1:
Bit voltage for Bit0 is 1 V (Volt);
Bit voltage for Bit1 is 2 V;
Thus:
Input code 00: 0+0=0 V;
Input code 01: 0+1=1 V;
Input code 10: 2+0=2 V;
Input code 11: 2+1=3 V.
Sequence 0, 1, 2, 3 V is linear.
Example #2:
If Bit0 resistor causes 0.1 V error, it produces 1.1 V instead 1.0 V,
and Bit1 resistor causes -0.2 V error, it produces 1.8 V instead 2.0 V.
Thus:
Input code 00: 0+0=0 V;
Input code 01: 0+1.1=1.1 V;
Input code 10: 1.8+0=1.8 V;
Input code 11: 1.8+1.1=2.9 V.
Sequence 0, 1.1, 2, 3.1 V is non-linear.
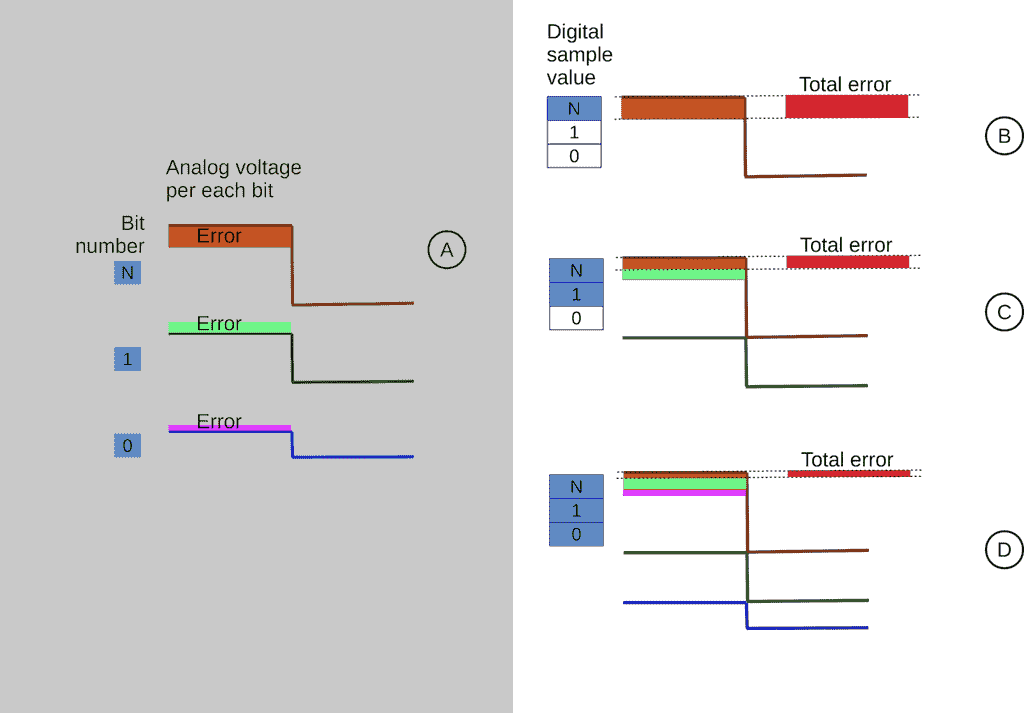
In other words, the non-linearity is error altering by input PCM code. In the picture below, let's see the dependency of the "Total error" value of several bits of input PCM code).
DAC non-linear distortions. The error level depends on input PCM code
Warning: Calculations below are intended for approximate estimation only.
If R2R DAC has N bit input, its approximate noise level is:
NSL = 20 * log10(1/2N-1).
For 16-bit DAC a noise level 96 dB is expected.
But, actually, the level is about -110 dB due to averaging and distributing in Furie transform discrete frequency positions.
Each of the bit resistors causes an error in voltage before the analog filter in conformance resistor precision.
Voltage error may be estimated by the formula:
Verr=Vin*R2/(RNbit+R2)-Vin*R2/(RNbit*(1+rerr/100%)+R2),
where:
Verr - absolute voltage error for Nth bit;
Vin - input logic voltage value on a bit;
R2 - common DAC resistor connected with the ground;
RNbit - resistor in bit circuit (receive the logic voltage);
rerr - RNbit resistor error in percent.
According to the formula, the most significant impact on absolute voltage error Verr causes resistors of the highest bits.
Maximum voltage level before the analog filter (when all bits in logic "1") is Vin*(1-21-N) and may be accepted as equal Vin.
It works when bit #[N-2] gives 0.5*Vin level and bit #[N-1] changes the polarity of the output voltage.
To compare with noise, the error is normalized in dB:
Verr dB = 20 * log10( Ve / Vin ).
In the table, the caused error is shown for each of the resistors from bit #8 to #14.
16-bit resistor DAC
Resistors with 0.05% tolerance are precise enough at the modern technology level.
But we can see that 0.05% tolerance causes errors with level values above the noise, which was accepted at -110 dB above.
As example, bit #14 causes error Verr dB -78 dB. It is 32 dB over the noise level.
If we refer to measurements practice, deviation of generated voltage value should cause errors 3...10 times (not in dB) lesser than lowest bit (#1) value -96 dB. I.e. higher bits (#1 and above) should not mask work of lowest bit (#0).
But the author would suggest comparing the deviation with the quantization noise level. Because the lowest bit is changed in time.
Thus errors Verr dB should cause dB error below -110 dB.
Let's look at voltage error with 0.0005% resistor tolerance:
As the author knows, resistors with 0.0005% tolerance are most precise at the moment of the article writing [1].
Bit #14 causes error Verr dB -118 dB. It is 8 dB below the quantization noise level.
So 16-bit ladder DAC may be implemented on 0.0005% tolerance resistors.
Unfortunately, except for the tolerance, the resistor value depends on temperature. Temperature is defined by environmental temperature and current that pass through the resistor.
Also, the bit input voltage is switched by electronic keys. These keys also cause voltage error that depends on temperature too.
Let's consider 24-bit resistor DAC now:
24-bit resistor DAC
| Bit number | Caused maximal error Verr dB in dB(Vin) |
|---|---|
| 22 | -78 |
| 21 | -81 |
| 20 | -85 |
| 19 | -91 |
| 18 | -96 |
| 17 | -102 |
| 16 | -108 |
Here we can view values the same for 16-bit resistor DAC. Because the same resistor values are used in the highest bits.
However, for 24-bit resistor DAC these errors should be compared with -144...-150 dB quantization noise.
PCM DAC with sigma-delta modulator
The aforementioned resistor DACs have output non-linear distortion issues due to resistor value deviation and temperature.
To solve the issue we can reduce the number of bit resistors. It allows to build DAC easier way and reduces the impact of resistance temperature stability.
Using an intermediate sigma-delta modulator is a way of reducing the resistor number.
PCM signal is oversampled and converted (into the digital domain) to sigma-delta modulated one. Analog filtration at output removes the modulation noise of the sigma-delta modulator. At output audio signal, restored from digital form, is present.
For this DAC type resistor value deviation doesn't cause non-linear distortions. It only impacts to total amplitude value of an analog signal.
However, oversampler with digital filter has alias issue and sigma-delta modulator has issues with overload tolerance.
DSD DAC vs PCM DAC sigma-delta based
DSD DAC doesn't contain oversampler and sigma-delta modulator modules with their issues.
DSD DAC
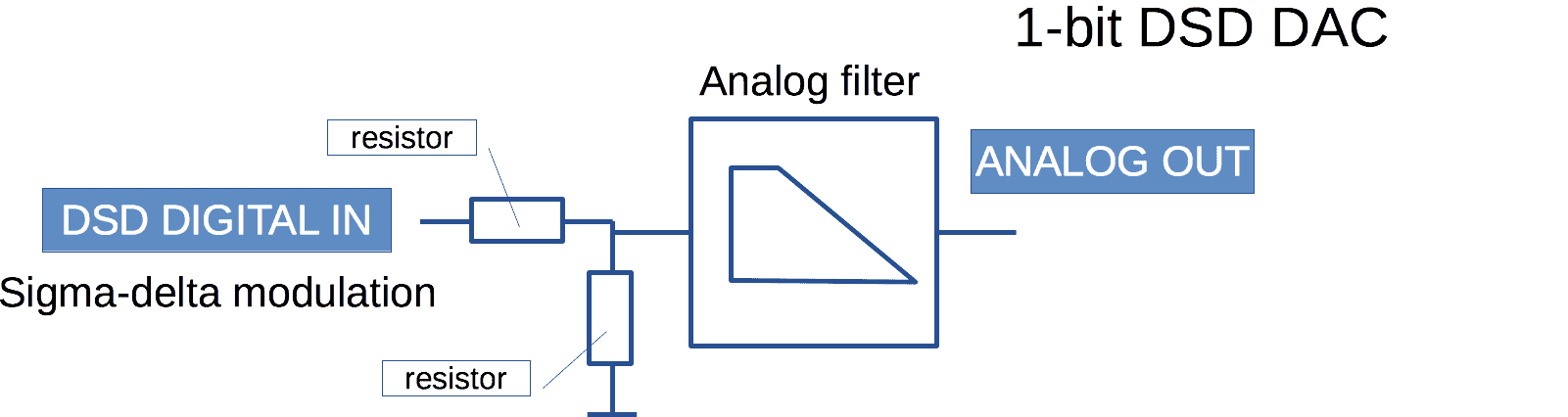
In DSD DAC resistor value deviation doesn't cause non-linear distortion. Input voltage modulation can cause non-linear distortions though. But it may be fixed via filtering of power line and other. PCM DAC has the same issues too.
The main feature of DSD recording or PCM to DSD conversion is noise shaping (pushing quantization noise energy out of audible range).
Noise shaping defines the low border of the frequency range where the DSD-modulation-noise spectrum has significant level growth. In the picture below the "low border" is the most left point of "modulation noise" shape at the "frequency" axis.
The higher-frequency border of the modulation noise (in the picture above, part B) provides better suppression of DSD noise for the same analog filter.
Because noise is pushed in the frequency range, where analog filter provides higher suppression.
But on the other hand, the higher border can cause lesser tolerance to overload at sigma-delta modulator input. I.e. there is more probability, that sigma-delta modulated stuff will be damaged by overload. It does not matter of DSD DAC though.
Back to topNOS DAC. Non-oversampling digital-analog converter
Non-oversampling DAC is a way to rid ringing artifacts and other distortions, that are caused by digital filtering inside DAC.
It is the usual DAC without oversampler.
Read details about NOS DAC >
Back to top
Conclusions
- In the general case, binary-weighted and R2R resistor DACs are tougher in design and adjusting, than PCM DACs that are based on sigma-delta modulators.
- Minimal DSD DAC has no oversampling/digital filtering and sigma-delta modulator stages. Thus it is easier than any kind of PCM DAC.
- DSD DAC has useful band limitation due to the band reserve that is required for the noise shaping. The useful band expansion may be solved via a higher oversampling ratio into the DAC.
- Real DACs are more complex devices than their concepts (A, B, C, D parts in the "DAC type comparison" picture). The concepts give engineers potential design abilities only. DAC type on its own doesn't guarantee better/worse quality.
Back to top
DAC list
R2R DAC list
R2R DAC list [check out music samples]
| Name | Sample rate / Bit depth | Inputs | Outputs | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mu |
up to 24 bit / 192 kHz; 1536 kHz; DSD64, DSD1024 | SPDIF RCA, Optical, USB, AES/EBU, I2S via HDMI LVDS | RCA, XLR | Non-Oversampling NOS / Oversampling |
| Schi |
up to 24 bit / 192 kHz | AES/EBU XLR, RCA SPDIF |
XLR balanced, RCA | |
| Schi |
up to 24 bit / 192 kHz | USB, Toslink SPDIF, Coaxial SPDIF | RCA stereo | |
| SMSL AUDIO VMV D3 | up to 32 bit / 768 kHz; native DSD512 | SPDIF RCA, optical, I2S, Clock, USB, AES/EBU | Balanced, RCA | [Manual] |
| Sonnet Morpheus MK-II | up to 24 bit / 384 kHz | SPDIF optical, coaxial, AES / EBU, USB | XLR balanced, RCA stereo | NOS, MQA module optional |
| Vin |
up to 24 bit / 192 kHz; 1536 kHz; DSD64, DSD1024 | SPDIF RCA, optical, USB | RCA, XLR | Non-Oversampling NOS / Oversampling |
| Vin |
up to 24 bit / 192 kHz; 1536 kHz; DSD64, DSD1024 | SPDIF RCA, Optical, AES/EBU, USB, I2S via HDMI LVDS, I2S via RJ45 LVDS, I2S via RJ45 LVCMOS | RCA, XLR | Non-Oversampling NOS / Oversampling |
R2R ladder (or Multiplying) DAC scheme is intended for multibit PCM only. DSD DAC has no multibit issues and it's simpler in resistors.
DSD DAC list
DSD DAC list [check out music samples]
| Name | Sample rate / Bit depth | Inputs | Outputs | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACCUSTIC ARTS PLAYER I | up to 24 bit / 192 kHz; DSD128 | SPDIF coaxial, optical, USB | XLR balanced, RCA | [Brochure] |
| Cam |
up to 24 bit / 768 kHz; up to DSD512 native; MQA | 2 x SPDIF coaxial, optical, USB | Headphones, XLR balanced, RCA | [Manual] Bluetooth v4.2, A2DP profile, SBC, AptX |
| Chord Qutest | up to 32 bit / 768 kHz; up to DSD512 native | USB, 2 x BNC, SPDIF optical | RCA | [Manual] |
| iFi iDSD Diablo | up to 768 kHz; up to DSD512; up to double-speed DXD; MQA | USB, SPDIF coaxial/optical | Balanced 4.4mm | [Manual] |
| iFi Pro iDSD Signature | up to 768 kHz; up to DSD1024; up to double-speed DXD, MQA | USB, AES3, S/PDIF coaxial/optical combo, BNC multifunction S/PDIF in or sync input | Balanced XLR, Single-Ended RCA, Headphones 6.3mm & SE 3.5mm jack, Headphones BAL 4.4mm jack, Headphones out | [Manual] |
| iFi Zen Air | up to 384 kHz; up to DSD512; MQA renderer | USB | RCA | [Manual] |
| Mu |
up to 24 bit / 192 kHz; 1536 kHz; DSD64, DSD1024 | SPDIF RCA, Optical, USB, AES/EBU, I2S via HDMI LVDS | RCA, XLR | Non-Oversampling NOS / Oversampling, R-2R |
| SMSL AUDIO VMV D3 | up to 32 bit / 768 kHz; native DSD512 | SPDIF RCA, optical, I2S, Clock, USB, AES/EBU | Balanced, RCA | [Manual] |
| Vin |
up to 24 bit / 192 kHz; 1536 kHz; DSD64, DSD1024 | SPDIF RCA, Optical, USB | RCA, XLR | Non-Oversampling NOS / Oversampling, R-2R |
| Vin |
up to 24 bit / 192 kHz; 1536 kHz; DSD64, DSD1024 | SPDIF RCA, Optical, AES/EBU, USB, I2S via HDMI LVDS, I2S via RJ45 LVDS, I2S via RJ45 LVCMOS | RCA, XLR | Non-Oversampling NOS / Oversampling, R-2R |
Back to top
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of DAC?
DACs have different types:
- sigma-delta,
- binary-weighted,
- R2R-ladder,
- non-oversampling.
What is R2R DAC?
R2R DAC is a DAC based on a resistor matrix, which forms output voltage according to a sample code of digital signal.
As example, a digital audio signal, comes from a computer.
What is R2R audio?
R2R is related to PCM DACs whose design is based on resistors with values R and 2R.
What is R 2 R DAC?
R2R is a digital-to-audio converter's architecture which is built on resistors with values R and 2R.
What is an R to R DAC?
The more correct term here is "R2R". Such DACs are designed on resistors. They have values as R as 2R.
What does R2R mean in a DAC?
"R2R" means a circuit with resistors with R and 2R values. This circuit architecture is used in digital-to-audio converters.
What is Delta Sigma DAC?
What is a Sigma Delta DAC?
Delta-sigma DAC converts DSD digital audio signal to analog one.
PCM digital-to-analog converter may be implemented on the sigma-delta principle. Otherwise, PCM DAC is based on a resistor matrix.
Read more...
What is FPGA DAC?
FPGA is A Field-Programmable Gate Array. It's a programmable electronic scheme. It may be used to build a DAC.
Is Delta-Sigma DAC good?
In the first approach, delta-sigma DAC is capable to convert digital to analog signal easier way for high sound quality.
What is a ladder DAC?
A ladder DAC is R2R DAC. Its scheme is like to "ladder" from resistors.
What is r2r ladder type?
A ladder DAC is R2R DAC. Its scheme is like to "ladder" from resistors.
Is Multibit a R2R?
Both R2R ladder and sigma-delta DACs are multi-bit digital-to-analog converters.
However, sometimes, R2R is considered as multi-bit DAC.
What is Multibit DAC?
Multibit DAC is digital-to-analog converter that transform digital multibit PCM audio to analog one.
Also, "Schiit Audio" calls their ladder R2R DACs "multibit".
What are the advantages of R2R ladder DAC?
At first sight, R2R DAC has a simpler design advantage. I.e. lesser element lesser distortions.
There is no sigma-delta modulator, oversampler, that can cause ringing.
However, simplicity requires the greatest precision of the components, constructive and montage. It may not (or almost may not) be achieved for home devices. At least, it requires a big time of manufacturing, including adjusting.
And, in ordinary conditions of work, the temperature and the humidity variate parameters of such converter scheme. The variations cause distortions.
What are three advantages of R 2R ladder DAC?
The author knows only these advantages:
- R2R DAC looks simple.
- Minimum resistor values make manufacturing simpler, comparing binary-weighted DAC.
What is the advantages of R 2R ladder DACs over those that use binary-weighted resistors?
The main advantage R2R digital-to-analog converter over binary-weighted resistors is a lesser range of resistor values. It's easier in delivery for manufacturing.
However , let's remember, that binary weighted scheme may be implemented on R and 2R resistors.
Read more...
What is the major advantage of R 2R ladder D A converter as compared to binary weighted resistors?
R2R ladder DAC contains only 2 resistor values. It's cheaper and easier for manufacturing.
Read more...
How does a R2R ladder works?
R2R DAC contains a resistor matrix, that converts input code (value of sample) to voltage. After it, a sequence of voltage values passed through an analog filter, that smooths the output voltage. To be exact, the smoothing is calling as "interpolation" and filter remove aliases of the "stair-step" signal.
How does r2r ladder DAC work?
R2R ladder DAC is based on a ladder of resistors. Inputs of the ladder is refer to bites of PCM sample.
With the ladder, different bit combinations produce different voltage levels.
What is a weighted resistor DAC?
Weighted resistor DAC (or R2R, ladder) is DAC based on a resistor matrix. The matrix contains several resistors.
1 resistor is fed by 1 bit of input code (of a sample of a digital audio signal). The resistors have different electrical resistance (weight).
The resistance value causes different values of the output voltage.
The sequence of the voltage values forms an analog audio signal from the sequence of codes (PCM digital signal) at the input of the DAC.
Are R2R DACs better?
Why is R-2R ladder DAC a better choice?
Is R2R DAC better?
In general case, R2R DAC has disadvantages rather from an engineer point of view. It happens because the required resistor precision to provide allowable non-linear distortions.
Read more...
Do R2R DACs sound better?
Does R2R DAC sound better?
The general recommendation is to listen to both R2R and sigma-delta DACs and make your choice.
Is R2R better than Delta Sigma?
Sigma-delta PCM DAC solves non-linear distortion issues, that R2R DAC causes.
However, the final result is a matter of how both units are done.
Read details...
What are the advantages of R-2R ladder DAC? What are the advantages of R-2R DAC?
R2R DAC's advantage is it may be assembled from several resistors. Even, without active elements, like transistors. It looks like a minimalistic ideally-linear device with an extremely low own noise floor. However, the issues are there.
Read about it...
What is the major advantage of the R 2R ladder?
The main advantage of R2R ladder DAC is the apparent simplicity and minimum elements that can cause distortions. However, some issues are there. Read more...
Why is R 2R ladder DAC a better choice? Are R2R DACs any good?
Abstract R2R ladder DAC is not a better choice. Theoretically, sigma-delta DAC is more linear. But, an alternative unit with a sigma-delta modulator is not ideal.
Except a resistor matrix and sigma-delta modulator, a DAC contains other parts that are important for sound quality.
And we should compare real devices in both types to find a better option.
Read more...
What are the disadvantages of R2R ladder DAC?
A ladder DAC disadvantages, comparing sigma-delta digital-analog converter, are:
- non-linearity due to resistor precision and stability;
- precision and stability of matrix switchers;
- more sophisticated manufacturing.
Read more...
What is the main disadvantage of weighted resistor DAC?
In common case, a weighted resistor DAC has several important disadvantages, in contrast, sigma-delta converter:
- higher non-linearity due to precision and stability of resistors;
- matrix switcher's stability and precision;
- harder adjusting.
Read more...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of R 2R ladder type DAC?
An R2R ladder DAC has these advantages and disadvantages.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of DAC?
DAC advantages and disadvantages are depending on its type. In instance, you can read about the advantages and disadvantages of a ladder DAC comparing a sigma-delta one.
What is NOS R2R DAC? Who makes R2R DACs?
Look at the NOS DAC list...
What is the difference between binary weighted and R 2R ladder?
R2R ladder DAC consists of resistors with R and 2R values in the main circuit. Binary weighted DAC is based on the values R, 2R, 4R, ..., 2NR. Read more...
What is the advantage and disadvantage of R 2R ladder DAC over the binary weighted resistors DAC?
Binary-weighted resistor DAC required move values of resistors than R2R one. R2R DAC requires only 2 values for level forming circuit.
Binary-weighted DAC may be built on 1 or two resistor values, but it will require more components of the DAC.
Why is an inverted R 2R ladder network DAC better than R 2R ladder DAC?
Inverted R2R DAC is slightly simpler in basic scheme than non-inverted one.
The advantages and disadvantages of different DAC types see here...
What is the role of op amp in R-2R ladder DAC circuit?
In R-2R ladder DAC, the operational amplifier is intended to unbind the resistance of ladder matrix and the resistance of load (an audio device) that is connected to the DAC output.
Without the amplifier, the load will impact to the voltage at output of this resistor ladder.
Also, the operational amplifier set amplitude at the DAC output.
Why do R2R DACs sound better?
Technically, sigma-delta DAC is better than a ladder one. An R2R DAC has advantages and disadvantages. Practically, we do not compare abstract DAC concepts, but their implementations.
Compared implementations may be done differently. And their sound is different.
Also, "sound better" term is located in a human brain. And it can interpret higher distortions with certain characters as better sounding.
Who makes R2R DACs?
On the market, you can find R2R ladder DACs:
- Musician Audio Pegasus,
- Musician Aquarius,
- Denafrips Ares2,
- Metrum Amethyst,
- others.
Is Schiit Multibit R2R? Is Schiit a R2R?
Schiit Multibit DAC is designed on AD5547 chip. It's multiplying DAC.
Multiplying DAC is a ladder (R2R) DAC subtype, that is commutating resistors to set output values. See example.
Shiit Yggdrasil is based on Texas Instruments DAC8812 chip. The chip is multiplying and contains R2R ladder scheme.
Which is the fastest ADC and why?
Flash ADC type is the fastest analog-to-digital converter. Each digitized input-signal level is compared individually. So, 2-bit ADC contains 4 comparators.
Read also: Power Conditioner. Do You Have Audio Quality Benefits? [Explained] >
Back to top
Music samples for test DAC abilities
To check how digital-to-audio converter works, download for free audio files in these resolutions:
Back to top
References
Audio Basis - articles about audio
Back to top