

Back to top
How to normalize audio (auto maximize peak level)
To normalize audio peak volume level:
- Launch AuI ConverteR software
- Push "Open files" button and open the files.
- In the left part of the main window, click "Levels tab".*
- In the "Level adjusting" list, select "To peak" (normalize peak audio level).
The "peak" here is the maximum level in file. Each file has its own peak. - If you want to correct only peaks above the level (see goal 6), uncheck "Correct always" switch.
- Set target peak level value in dB via the slider or edit box.
- Select "Per file" or"Per directory" (by album) or "Total" (all converted files)
- Push "Start" button and wait for the conversion end.

* Try in FREE version. Audio normalization is fully supported in configurations
Read how it works >
Back to topHow to normalize audio (auto set average level)
To normalize the average loudness (ITU-R BS.1770) of audio files:
- Launch AuI ConverteR software
- Push "Open files" button and open files.
- Click "Levels tab"* in the left part of the main window.
- In the "Level adjusting" list, select "To average" (normalize average audio level).
- Check "No overload" to provide normalization to the average level without overload, if the average level is set too high.
When overload, the actual average level will decrease below target level (see goal 6). - Set target average level value in dB via the slider or edit box.
- If "No overload" is checked, select "Per file" or "Per directory" (by album) or "Total" (all converted files)
- Push "Start" button and wait until the conversion end.
* Try in FREE version. Audio normalization is fully supported in configurations
WARNING:
DVD-audio/video, Blu-Ray, DVD/BluRay/CD ISO are NOT supported.
For Modula-R version, SACD ISO, DSF, DFF are supported in proper configurations.
For ISO tracks, DSF, DFF longer than 3 minutes, FREE edition mutes 2-second silence in the output middle and has other restrictions. In batch conversion FREE version mutes 2 seconds in the output middle for second and the subsequent files.
Free version has processing sound quality identical commercial editions.
Read how the audio normalizing works...
Back to top
How to set file level manually
Alternatively, you can use manual gain control and/or fixed-step attenuator in the program settings.
Read more...
Back to top
Overload reasons for audio conversion
The headroom (as rule 6 dB) is used for stable work of sigma-delta modulator (DSD encoder).
We can imagine audio signal as water in a pool.
We can pour water into the pool until its level achieves the pool edge.
After it, the water level may not be increased via the water pouring.
It's called overload or level clipping.
An audio signal (music) is like a wave on the pool surface.
If the wave is too high, it will pour out of the pool.
So, we can limit the wave height, to avoid water loss due to overflowing (overload).
The limit is called "headroom" for audio.
Sigma delta modulator due to overload can lose stability. It can be heard as continuous tone. Stability can be restored by resetting the encoder.
However, sometimes loudness increase is possible without instability of DSD encoder.
If input audio signal has an amplitude near maximum, upsampling can cause overload.
Let look at the picture:
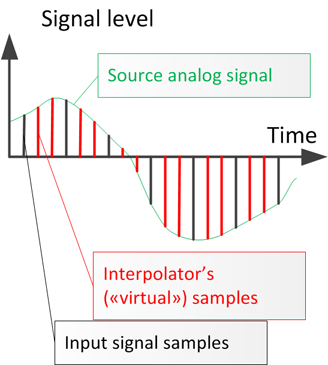
After upsampling (oversampling) between real samples of original signal appears "virtual" samples that appear due interpolation.
Amplitudes of some "virtual" samples can be upper than original samples. If peak level of original samples near maximal allowable value, "virtual" samples can be upper the value.
It can cause overload.
Back to top
How to normalize peak level audio and avoid overload
For avoiding same overloading during audio conversion need perform correction of output file levels.
Such conversion executed in 2 stages:
1. Measurement real output peak levels after audio conversion
2. Correction levels of output files.
Example 1 (normalizing audio with overload avoiding):
Output file #1 have peak level -1 dB.
Output file #2 +2 dB.
Maximum peak level here +2 dB.
For avoiding overload need decrease level of output file #2 at 2 dB. It will have peak level 0 dB (= +2 dB - 2 dB).
Output file #1 level need decrease at 2 dB too. It will have peak level -3 dB (= -1 dB - 2 dB).
Example 2 (normalizing audio with loudness maximizing):
Output file #1 have peak level -1 dB.
Output file #2 -2 dB.
Maximum peak level here -2 dB.
Here possible increase level of both output files. Output file #1 at 1 dB. It will have peak level 0 dB (= -1 dB + 1 dB).
Output file #2 level need increase at 1 dB too. It will have peak level -1 dB (= -2 dB + 1 dB).
Back to top
How to normalize audio for group of albums
Sometimes need total normalize peak loudness for several albums. Album here is either folder with songs or ISO-file or CD.
AuI ConverteR found peak levels for all tracks of all albums.
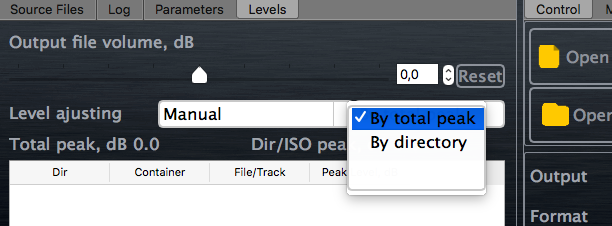
There are 2 ways maximizing loudness with avoiding of overload:
- Equalize levels by total peak level of all tracks in all albums (see picture below: By total peak).
- For each album equalize levels by peak level of the album (By directory).
Back to top
AuI ConverteR's level control modes
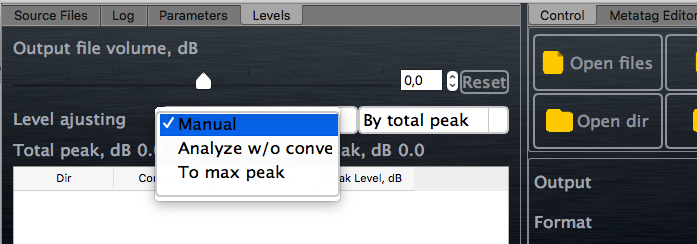
1. Manual
Volume don't auto adjusted during conversion. Read more...
2. Analyze without converting
Analyzing level of output audio files without recording it to hard disk. Results will displayed at table in Levels tab of main window of AuI ConverteR 48x44.
To display average level (EBU R128),
in Settings > BWF > check "Calculate loudness EBU R128 (ITU-R BS.1770) [WARNING: works slower]".
NOTE: The checked state cause lower speed of level calculation.
3. To max peak
Auto maximizing peak levels output files without overload. How it work see here and here.
4. To average
Auto normalizing to average level (EBU R128). Read how it works.
AuI ConverteR is a configurable software that lets you choose the features you need and pay only for them. A "module" is a part of AuI ConverteR's functionality that you can buy separately. You can buy new modules later to enhance your Modula-R major version (details). Each module is a license key that you get by email and enter in the software. A "major update" is a change in the first version number of the software version (for example, from 10.x to 11.x) and it is not free. However, your license is unlimited-time, which means you can use the software as long as you want without any subscription fees. (details)
IMPORTANT: The Free version of AuI ConverteR does not work with any modules. You need to buy a CORE module first, and then you can add other modules that are compatible with it (details). If you buy all the modules, you get the same features as the PROduce-RD version, which is a complete and cheaper package. You cannot exchange your Modula-R license for a PROduce-RD license.
* All prices on this page are in U.S. dollars without V.A.T. and other applicable taxes and fees. The prices are recommended. Information on this page is not a public offer.
Remarks:
- Auto loudness normalization applied in PROduce-RD edition only (in Modula-R edition as option Auto Level Normalization add-on).
- Output file volume slider counted during all modes. For PROduce-RD edition Output file volume slider placed in Parameters tab of main window of AuI ConverteR 48x44.
- For conversion to DSF files forced small (about -0.4 dB) additional attenuation for better stability of sigma delta modulator.
- Stability troubles (tone(s) or silence in recording) linked with overload of sigma delta modulator (for to DSF conversion). After breaking of stability, it is not restored during end of file.
Allowable maximal peak level of signal encoded to DSF can cause stability troubles sometimes.
Stability depend on impact time of maximal level to input of DSD encoder.
If AuI ConverteR have stability troubles to you files recommended use additional attenuation: in Settings window (push Settings button in main window) > General tab need set for switch Sigma delta modulator attenuator value discrepant zero.
More attenuation (more negative number) - less probability of breaking stability of DSD encoder.
However, it decrease loudness of converted file too.
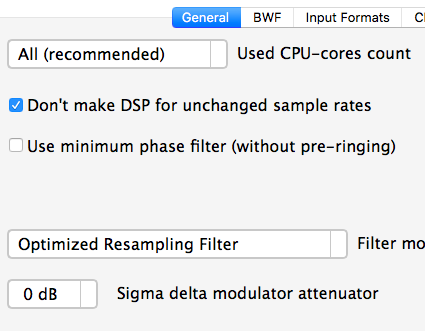
You can set auto restoring of average default level (reset).
In Settings > Interface > check "Save level normalization state after restart" switch.
In Settings > General > set value of "Default normalization level, dB [average normalization audio]" input field.
Back to top
Does normalizing audio affect quality?
In the first approach, normalizing like any gain control does't affect audio quality. It the gain control is done properly.
However, level decreasing degrade signal/noise ratio for sound recording. This could have implications for very quiet music fragments.
Read more...
Back to top
Frequently Asked Questions
What does normalizing an audio do?
Normalizing audio do level equal target value. In instance, all album tracks have different average levels. We are select level that we want (target level). And, make equalization of all track levels to target one.
Read more...
Is it good to normalize audio?
Audio normalization is elementary procedure - gain altering. If it done properly, it don't cause distortions that we can detect even via analysis.
Read more...
When should you normalize audio tracks?
For some applications of professional audio, requirements exist.
As example:
TV advertizing should provide certain level. Otherwise, the advertising may sound too loud.
For DSD audio, peak level should have headroom -6 dB. Otherwise, it can cause overload and broken stability of some DSD modulators.
When you listen playlist, different tracks may have different levels. It can cause discomfortable listening. You can equalize all average levels of the tracks, and listening may become more comfortable.
Read more...
Can VLC normalize audio?
Yes. VLC player can normalize audio. More...
How do I normalize audio volume?
To normalize audio volume, average-level normalizing is required rather. Read more...
How do you flatten audio to the same volume level?
To "flatten" or normalize audio volume level, use normalizing by average level.
Read more...
Does YouTube normalize audio?
As far as is known, YouTube normalize too loud audio. Read discussion...
How can I improve the sound quality of a video?
You can compress audio, apply equalization (EQ), reduce noise, etc.
What dB should video audio be?
Peak level of an audio track should not be above 0 dB. Sometimes, headroom (peak level reserve) is required. In instance, -3 dB is target maximum peak level.
Read more...
Back to top